Biology:Outline of Uruguay
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Uruguay:
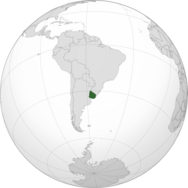
Uruguay – sovereign country located in southeastern South America.[1] It is home to 3.46 million people, of which 1.7 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area. Montevideo was founded by the Spanish in the early 18th century as a military stronghold. Uruguay won its independence in 1825-1828 following a three-way struggle between Spain , Argentina and Brazil. It is a constitutional democracy, where the president fulfills the roles of both head of state and head of government. The economy is largely based on agriculture (making up 10% of GDP and the most substantial export) and the state sector, Uruguay's economy is on the whole more stable than in its surrounding states, and it maintains a solid reputation with investors.
General reference
- Pronunciation: (/ˈjʊərəɡwaɪ/ (
 listen); Spanish: [uɾuˈɣwaj])
listen); Spanish: [uɾuˈɣwaj]) - Common English country name: Uruguay
- Official English country name: The Oriental Republic of Uruguay
- Common endonym(s): Uruguay
- Official endonym(s): República Oriental del Uruguay
- Adjectival(s): Uruguayan
- Demonym(s): Oriental, Uruguayan
- Etymology: Name of Uruguay
- International rankings of Uruguay
- ISO country codes: UY, URY, 858
- ISO region codes: See UY
- Internet country code top-level domain: .uy
Geography of Uruguay
Geography of Uruguay
- Uruguay is: a country
- Location:
- Southern Hemisphere
- Western Hemisphere
- Latin America
- South America
- Southern Cone
- South America
- Latin America
- Time zone: UTC-03
- Extreme points of Uruguay
- High: Cerro Catedral 514 m (1,686 ft)
- Low: South Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: 1,648 km
 Brazil 1,068 km
Brazil 1,068 km Argentina 580 km
Argentina 580 km
- Coastline: South Atlantic Ocean 660 km
- Population of Uruguay: 3,340,000 - 132nd most populous country
- Area of Uruguay: 176,215 km2
- Atlas of Uruguay
Environment of Uruguay
- Climate of Uruguay
- Renewable energy in Uruguay
- Geology of Uruguay
- Protected areas of Uruguay
- National parks of Uruguay
- Wildlife of Uruguay
- Fauna of Uruguay
- Birds of Uruguay
- Mammals of Uruguay
- Fauna of Uruguay
Natural geographic features of Uruguay
- Fjords of Uruguay: none
- Glaciers of Uruguay: none
- Islands of Uruguay
- Lakes of Uruguay
- Mountains of Uruguay
- Volcanoes in Uruguay: none
- Rivers of Uruguay
- Valleys of Uruguay
- World Heritage Sites in Uruguay: Colonia del Sacramento
Regions of Uruguay
Regions of Uruguay
Ecoregions of Uruguay
List of ecoregions in Uruguay
Demography of Uruguay
Demographics of Uruguay
Government and politics of Uruguay
Politics of Uruguay
- Form of government: presidential representative democratic republic
- Capital of Uruguay: Montevideo
- Elections in Uruguay
- Political parties in Uruguay
Branches of the government of Uruguay
Government of Uruguay
Executive branch of the government of Uruguay
- Head of state: President of Uruguay,
- Head of government: President of Uruguay,
- Cabinet of Uruguay: consisting of the President of the Republic and the Ministries
- Ministry of Economy and Finance
- Ministry of Education and Culture
- Ministry of Environment
- Ministry of Foreign Relations
- Ministry of Housing and Territorial Planning
- Ministry of Industry, Energy and Mining
- Ministry of the Interior
- Ministry of Labour and Social Welfare
- Ministry of Livestock, Agriculture, and Fisheries
- Ministry of National Defense
- Ministry of Public Health
- Ministry of Social Development
- Ministry of Transport and Public Works
- Ministry of Tourism
Legislative branch of the government of Uruguay
- Parliament of Uruguay (bicameral)
- Upper house: Senate of Uruguay
- Lower house: Chamber of Deputies of Uruguay
- Other dependencies of the Parliament of Uruguay:
- National Institute for Human Rights and Ombudsman
- Parliament Commissioner for the Penitentiary System
Judicial branch of the government of Uruguay
Court system of Uruguay:
- Supreme Court of Uruguay: highest tier of courts under the Judicial branch.
- Courts of Appeals: second highest tier of courts under the Judicial branch. It includes Civil, Criminal, Family, and Labour courts.
- District Courts (or Lawyer Courts): in Montevideo these are Bankruptcy, Civil, Contentious Administrative, Criminal, Criminal (Organized Crime), Criminal (Penitentiary Surveillance), Customs, Family, Family (Specialized), Juvenile, and Labour courts. In the interior of the country these are organized according their territorial jurisdiction (with at least two of them in each territorial jurisdiction), being assigned several subject matters to each of them.
- Peace Courts: courts of Montevideo, courts of the Interior's Departments' capitals, courts of cities and villages, rural courts.
- Other courts: Misdemeanor Courts, Conciliation Courts, Mediation Centers.
Foreign relations of Uruguay
Foreign relations of Uruguay
- Diplomatic missions in Uruguay
- Diplomatic missions of Uruguay
International organization membership
The Eastern Republic of Uruguay is a member of:[1]
|
|
Law and order in Uruguay
Law of Uruguay:
- Constitution of Uruguay
- Laws of Uruguay:
- Civil Code
- Penal Code
- General Procedure Code
- General Law on Private International Law
Human rights in Uruguay:
- LGBT rights in Uruguay
- Freedom of religion in Uruguay
Legal enforcement of Uruguay:
- National Police of Uruguay
Legal issues:
- Abortion in Uruguay
- Cannabis in Uruguay
Military of Uruguay
Military of Uruguay
- Command
- Forces
- Army of Uruguay
- Navy of Uruguay
- Air Force of Uruguay
Administrative divisions
Departments of Uruguay: the country is currently divided in 19 departments. Each department has an executive branch led by an intendant, and a legislative branch called Departmental Board.
- Artigas. Founded: 1884. Capital: Artigas. Area: 11928 km2.
- Canelones. Founded: 1816. Capital: Canelones. Area: 4536 km2.
- Cerro Largo. Founded: 1821. Capital: Melo. Area: 13648 km2.
- Colonia. Founded: 1816. Capital: Colonia del Sacramento. Area: 6106 km2.
- Durazno. Founded: 1822. Capital: Durazno. Area: 11643 km2.
- Flores. Founded: 1885. Capital: Trinidad. Area: 5144 km2.
- Florida. Founded: 1856. Capital: Florida. Area: 10417 km2.
- Lavalleja. Founded: 1837. Capital: Minas. Area: 10016 km2.
- Maldonado. Founded: 1816. Capital: Maldonado. Area: 4793 km2.
- Montevideo. Founded: 1816. Capital: Montevideo. Area: 530 km2.
- Paysandú. Founded: 1820. Capital: Paysandú. Area: 13922 km2.
- Río Negro. Founded: 1868. Capital: Fray Bentos. Area: 9282 km2.
- Rivera. Founded: 1884. Capital: Rivera. Area: 9370 km2.
- Rocha. Founded: 1880. Capital: Rocha. Area: 10551 km2.
- Salto. Founded: 1837. Capital: Salto. Area: 14163 km2.
- San José. Founded: 1816. Capital: San José de Mayo. Area: 4992 km2.
- Soriano. Founded: 1816. Capital: Mercedes. Area: 9008 km2.
- Tacuarembó. Founded: 1837. Capital: Tacuarembó. Area: 15438 km2.
- Treinta y Tres. Founded: 1884. Capital: Treinta y Tres. Area: 9676 km2.
Local government in Uruguay: since 2009 there is a new system of second level administrative divisions called "municipalities" in each department.
History of Uruguay
History of Uruguay
History of Uruguay, by period or event
- Indigenous peoples of Uruguay
- Charrúa people
- Guarani people
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata (1776–1814)
- Banda Oriental
- British invasions of the Río de la Plata (1806–1807)
- Liga Federal (1815–1820)
- Cisplatina (1821–1828)
- Thirty-Three Orientals
- Treaty of Montevideo (1828)
- Uruguayan Civil War (1839–1851)
- Uruguayan War (1864–1865)
- Paraguayan War 1864–1870
- Revolution of the Lances (1870–1872)
- Battle of Masoller (1904)
- Batllism
- Tupamaros
- Civic-military dictatorship of Uruguay (1973–1985)
- Law on the Expiration of the Punitive Claims of the State (1986)
History of Uruguay, by region
History of Uruguay, by subject
Political history of Uruguay
The history of Uruguay according to the political period (interim and other administrations in italics):
- Indigenous period: no political organization known.
- Colonial period and fight for independence.
- Nation building and prelude to civil war (1828-1839). Provisional governments of Suárez - Rondeau - Lavalleja. Presidencies of Pérez - Rivera - Anaya - Oribe - Pereira.
- Civil War (1839-1852). Presidency of Rivera (2nd). Simultaneous governments of Defensa (Suárez) and Cerrito (Oribe).
- End of civil war and politics of "fusion" (1852-1875). Presidencies of Berro - Giró. Triumvirate of Flores, Rivera and Lavalleja. Presidencies of Flores - Lamas (Montevideo only) - Bustamante - Pla - Pereira - Berro - Cruz Aguirre - Villalba. Dictatorship of Flores. Presidencies of Varela - Batlle y Grau - Gomensoro - Ellauri.
- Militarism and modernization (1875-1919). Presidency of Varela. Dictatorship of Latorre and his subsequent presidency. Presidencies of Vidal - Santos - Vidal (2nd) - Santos - Tajes - Herrera y Obes - Stewart - Idiarte Borda - Cuestas. Dictatorship of Cuestas. Presidencies of Batlle y Ordóñez - Cuestas - Batlle y Ordóñez - Williman - Batlle y Ordóñez (2nd) - Viera.
- Batlle reforms and modern Uruguay (1919-1933). Presidencies of Brum - Serrato - Campistegui - Terra.
- Authoritarian rule and end of collective head of government (1933-1943). Dictatorship of Terra. Presidency and brief dictatorship of Baldomir.
- Post WWII and period of prosperity (1943-1955). Presidencies of Amézaga - Berreta - Batlle Berres - Martínez Trueba. 1st National Council of Government.
- Economic decline, social conflicts and guerrilla (1955-1973). 2nd, 3rd and 4th National Council of Government. Presidencies of Gestido - Pacheco Areco - Bordaberry.
- Civic-military dictatorship of Uruguay (1973-1985). Rule by the Armed Forces and their allies. Regime of Bordaberry - Demicheli - Méndez - Álvarez.
- Return to democracy and present times (1985–present). Presidencies of Addiego - Sanguinetti - Lacalle - Sanguinetti (2nd) - Batlle - Vázquez - Mujica - Vázquez (2nd) - Lacalle Pou.
Culture of Uruguay
Culture of Uruguay
- Cuisine of Uruguay
- Disability in Uruguay
- Languages of Uruguay
- National symbols of Uruguay
- Coat of arms of Uruguay
- Flag of Uruguay
- National anthem of Uruguay
- Orders, decorations, and medals of Uruguay: the decorations granted by the Uruguayan authorities to distinguish persons or organizations due to meritory services or achievements.
- Civilian decorations:
- Medal of the Oriental Republic of Uruguay: a decoration granted to foreign individuals due to reciprocity reasons and diplomatic relationships.[2]
- Delmira Agustini Medal: granted to local or foreign individuals to distinguish their work and contribution to further improve the culture.[3]
- Order of Sports Merit: this decoration acknowledges individuals whose relevant merits or career path related to sports, locally or internationally, contributed with the development of the sports in Uruguay, and also to individuals who contributed with international covenants related to sports.[4]
- Medal of Military Merit: highest military award related to the Army of Uruguay, that awards civilian and military individuals, Uruguayan or foreign, and also to military units or institutions, due to meritory services or relevant contributions to the Army of Uruguay, and also for exceptional performance in combat in the case of military units.[5]
- Medal of Aeronautical Merit: highest military award related to the Uruguayan Air Force, that awards civilian and military individuals, Uruguayan or foreign, for their outstanding services in benefit of the Uruguayan Air Force or the national aviation.[6]
- Decoration Honor of Naval Merit Commander Peter Campbell: highest military award related to the Navy of Uruguay, that acknowledges civilian and military individuals, Uruguayan or foreign, and also to military units and Uruguayan or foreign institutions, for their outstanding services or relevant works served to the Uruguayan Navy.[7]
- 18 May 1811 Medal: second award in Army decorations hierarchy, to acknowledge meritory services to the Uruguayan Army.[8]
- 15 November 1817 Medal: second award in Navy decorations hierarchy, to distinguish civilian and military individuals, military units or institutions, for their merits related to the Navy.[9]
- Medal of Military Valor: third award in Army decorations hierarchy, to recognize heroic or valor in actions performed in duty.[10]
- Decoration General José Artigas Leader of the Orientals: decoration by the Staff of Defense office to distinguish individuals who contributed with their services to the Ministry of Defense, Staff of Defense office or to the branches of Armed Forces in general.[11]
- Civilian decorations:
- People of Uruguay
- Prostitution in Uruguay
- Public holidays in Uruguay: New Year's Day (1 January), Children's Day (6 January, commonly referred as Epiphany), Carnival (several days in February or March), Tourism Week (a week in March or April, also known as Holy Week), Landing of the 33 Patriots Day (19 April), Workers' Day (1 May), Anniversary of the Battle of Las Piedras (18 May), Birthday of José Artigas (19 June), Constitution Oath (18 July), Declaration of Independence (25 August), Day of the Race (12 October), Deceased ones Day (2 November), Family's Day (25 December, commonly referred as Christmas).
- Religion in Uruguay
- Christianity in Uruguay
- Roman Catholic Church in Uruguay
- Hinduism in Uruguay
- Islam in Uruguay
- Judaism in Uruguay
- Bahá'í Faith in Uruguay
- Christianity in Uruguay
- World Heritage Sites in Uruguay
Art in Uruguay
- Cinema of Uruguay
- Literature of Uruguay
- Music of Uruguay
- Television in Uruguay
Sports in Uruguay
Sports in Uruguay
- Football in Uruguay
- Uruguay at the Olympics
Economy and infrastructure of Uruguay
Economy of Uruguay
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 86th (eighty-sixth)
- Agriculture in Uruguay
- Banking in Uruguay
- Central Bank of Uruguay
- Communications in Uruguay
- Internet in Uruguay
- Companies of Uruguay
- Currency of Uruguay: Peso
- ISO 4217: UYU
- Energy in Uruguay
- Energy policy of Uruguay
- Nuclear energy in Uruguay
- Health care in Uruguay
- Mining in Uruguay
- Uruguay Stock Exchange
- Tourism in Uruguay
- Transport in Uruguay
- Airports in Uruguay
- Rail transport in Uruguay
- Roads in Uruguay
- Water supply and sanitation in Uruguay
Education in Uruguay
- Education in Uruguay: under the principles of compulsory, secular and free education of the public education institutions since 1876. The system comprises pre-primary education (compulsory from 4-year-old children), compulsory primary education, compulsory lower and higher secondary education, and voluntary tertiary education (university and not university).
- Universities in Uruguay:
- Public: University of the Republic, Technological University of Uruguay.
- Private: ORT University, University of the Enterprise, Catholic University, University of Montevideo, CLAEH University.
See also
- Uruguay
- Index of Uruguay-related articles
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of geography
- Outline of South America
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Portal/images/u' not found.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Uruguay". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/uruguay/.
- ↑ "Ley N° 16300. AUTORIZACION AL PODER EJECUTIVO A ACUÑAR LA "MEDALLA DE LA REPUBLICA ORIENTAL DEL URUGUAY" A LOS EFECTOS DE ENTREGARLAS A PERSONALIDADES EXTRANJERAS" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/leyes/16300-1992.
- ↑ "Ley N° 19050. CREACION DE "LA MEDALLA DELMIRA AGUSTINI"" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/leyes/19050-2013.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 148/997. CREACION DE LA ORDEN AL MERITO DEPORTIVO. DEPORTISTAS Y PERSONALIDADES DESTACADAS. COMISION NACIONAL DE EDUCACION FISICA" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/148-1997.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 511/991. CREACION DE LA MEDALLA AL MERITO MILITAR" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/511-1991.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 49/992. OTORGAMIENTO DE MEDALLA AL MERITO AERONAUTICO" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/49-1992.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 368/993. CONDECORACIONES. MEDALLA AL MERITO NAVAL" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/368-1993.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 71/019. DEROGACION DEL DECRETO 469/997 Y CREACION DE LA DISTINCION "MEDALLA 18 DE MAYO DE 1811"" (in es). IMPO. http://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/71-2019.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 43/000. CREACION DE LA MEDALLA 15 DE NOVIEMBRE DE 1817" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/43-2000.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 227/007" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/227-2007.
- ↑ "Decreto N° 372/013. CREACION DE LA DISTINCION "GRAL. JOSE ARTIGAS - JEFE DE LOS ORIENTALES"" (in es). IMPO. https://www.impo.com.uy/bases/decretos/372-2013.
External links
- General
- Uruguay. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Country profile of Uruguay by BBC News
- Maps
 |