Biology:RMF RNA motif
| rmf RNA | |
|---|---|
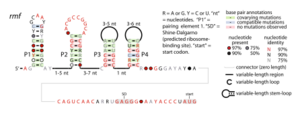 Consensus secondary structure of rmf RNAs | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | rmf RNA |
| Rfam | RF01755 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-regulatory element |
| Domain(s) | Bacteria |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The rmf RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was originally detected using bioinformatics.[1] rmf RNAs are consistently foundwithin species classified into the genus Pseudomonas, and is located potentially in the 5′ untranslated regions (5′ UTRs) of rmf genes. These genes encodes the ribosome modulation factor protein, which affects the translation of genes by modifying ribosome structure in response to stress such as starvation. This ribosome modulation is a part of the stringent response in bacteria. The likely biological role of rmf RNAs is ambiguous. Since the RNA could be in the 5′ UTRs of protein-coding genes, it was hypothesized that it functions as a cis-regulatory element. This hypothesis is bolstered by the observation that ribosome modulation factor binds ribosomal RNA, and many cis-regulatory RNAs called ribosomal protein leaders participate in a feedback regulation mechanism by binding to proteins that normally bind to ribosomal RNA. However, since rmf RNAs are not very close to the rmf genes, they might function as non-coding RNAs.
References
- ↑ "Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea and their metagenomes". Genome Biol 11 (3): R31. March 2010. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r31. PMID 20230605.
External links
 |

