Biology:RsaOG
| rsaOG RNA | |
|---|---|
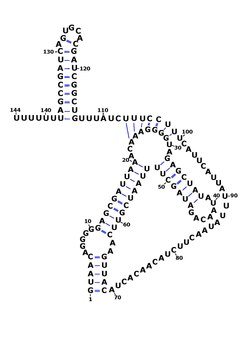 The consensus secondary structure of RsaOG showing its pseudoknot, created in Varna.[1] Boundaries were determined by RACE mapping in Staphylococcus aureus N315.[2] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RsaOG |
| Rfam | RF01775 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | sRNA |
| Domain(s) | Staphylococcus |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
RsaOG (an acronym for RNA S. aureus Orsay G)[2] is a non-coding RNA that was discovered in the pathogenic bacteria Staphylococcus aureus N315 using a large scale computational screening based on phylogenetic profiling.[3] It was first identified, but not named, in 2005.[4] RsaOG has since been identified in other strains of Staphylococcus aureus under the name of RsaI,[5] it has also been discovered in other members of the Staphylococcus genus (such as Staphylococcus carnosus) but in no other bacteria.[2]
The RsaOG gene is conserved in all Staphylococcaceae sequenced genomes, its secondary structure contains two highly conserved unpaired sequences which have the ability to form a pseudoknot.[2] Northern blot experiments show that RsaOG is expressed in several S. aureus strains.[3][5] Mapping of RsaOG ends indicates a size of 146 nucleotides in S. aureus.[5] RsaOG ncRNA is thought to have trans-acting regulatory functions, possibly on fine tuning toxin production or aiding with invasion.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure". Bioinformatics 25 (15): 1974–1975. August 2009. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp250. PMID 19398448.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "RsaOG, a new staphylococcal family of highly transcribed non-coding RNA". RNA Biol 7 (2): 116–119. March 2010. doi:10.4161/rna.7.2.10925. PMID 20200491. http://www.landesbioscience.com/journals/rna/abstract.php?id=10925. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Single-pass classification of all noncoding sequences in a bacterial genome using phylogenetic profiles". Genome Res. 19 (6): 1084–1092. June 2009. doi:10.1101/gr.089714.108. PMID 19237465.
- ↑ "Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102 (40): 14249–14254. October 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503838102. PMID 16183745.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "A search for small noncoding RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus reveals a conserved sequence motif for regulation". Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (21): 7239–7257. November 2009. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp668. PMID 19786493.
External links
 |
