Biology:SARS coronavirus X4 like protein domain
In molecular biology, SARS coronavirus X4 like protein domain is commonly shortened to SARS-X4. This protein domain is only found in viruses, specifically coronaviruses. X4 is the protein domain which is a unique type I transmembrane protein. It is named after the virus it was first discovered in, SARS-CoV, the virus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome.[1]
Function
The precise activity of SARS X4 like protein remains to be elucidated however it has been suggested that it has binding activity to integrin I domains.[2] Additionally it is thought to induce apoptosis via a caspase dependent pathway in different types of tissue; or in simpler terms, inducing cell death through an enzymatic pathway.[3] Also, it contains a motif which has been demonstrated to mediate COPII dependent transport out of the endoplasmic reticulum, and the protein is targeted to the Golgi apparatus. It remains unknown as to why the protein may be involved with cell trafficking.[4]
Structure
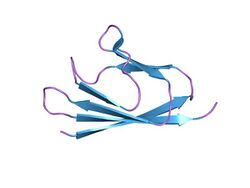
The structure of the coronavirus X4 protein (also known as ORF7a and U122) shows similarities to the immunoglobulin like fold despite the fact they do not share sequence similarity.[2] Their structure contains seven beta strands which form two beta sheets, compactly arranged in an immunoglobulin-like beta sandwich fold.[1]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 "Structure and intracellular targeting of the SARS-coronavirus Orf7a accessory protein.". Structure 13 (1): 75–85. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.10.010. PMID 15642263.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 "Solution structure of the X4 protein coded by the SARS related coronavirus reveals an immunoglobulin like fold and suggests a binding activity to integrin I domains". J. Biomed. Sci. 13 (3): 281–93. May 2006. doi:10.1007/s11373-005-9043-9. PMID 16328780.
- ↑ "The molecular biology of SARS coronavirus.". Ann N Y Acad Sci 1102 (1): 26–38. 2007. doi:10.1196/annals.1408.002. PMID 17470909. Bibcode: 2007NYASA1102...26S.
- ↑ "Structure, expression, and intracellular localization of the SARS-CoV accessory proteins 7a and 7b.". Adv Exp Med Biol. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 581: 115–20. 2006. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-33012-9_20. ISBN 978-0-387-26202-4. PMID 17037516.