Biology:Small nucleolar RNA SNORD67
| Small nucleolar RNA SNORD67 | |
|---|---|
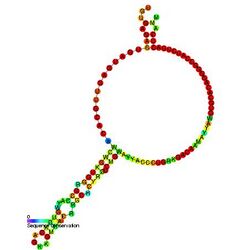 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of SNORD67 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SNORD67 |
| Alt. Symbols | snoHBII-166 |
| Rfam | RF00573 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; C/D-box |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | 0006396 0005730 |
| SO | 0000593 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
In molecular biology, SNORD67 (also known as HBII-166) is a non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecule which functions in the biogenesis (modification) of other small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). This type of modifying RNA is located in the nucleolus of the eukaryotic cell which is a major site of snRNA biogenesis. It is known as a small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and also often referred to as a guide RNA.
HBII-166 belongs to the C/D box class of snoRNAs which contain the conserved sequence motifs known as the C box (UGAUGA) and the D box (CUGA). Most of the members of the box C/D family function in directing site-specific 2'-O-methylation of substrate RNAs.[1]
snoRNA HBII-166 is the human orthologue of the mouse MBII-166[2] and is predicted to guide 2'O-ribose methylation of spliceosomal RNA U6 at residue C60.[3]
References
- ↑ "Purified box C/D snoRNPs are able to reproduce site-specific 2'-O-methylation of target RNA in vitro". Molecular and Cellular Biology 22 (19): 6663–8. October 2002. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.19.6663-6668.2002. PMID 12215523.
- ↑ "RNomics: an experimental approach that identifies 201 candidates for novel, small, non-messenger RNAs in mouse". The EMBO Journal 20 (11): 2943–53. June 2001. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.11.2943. PMID 11387227.
- ↑ "snoRNA-LBME-db, a comprehensive database of human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs". Nucleic Acids Research 34 (Database issue): D158-62. January 2006. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj002. PMID 16381836.
External links
 |

