Biology:Starry smooth-hound
| Starry smooth-hound | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Subdivision: | Selachimorpha |
| Order: | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family: | Triakidae |
| Genus: | Mustelus |
| Species: | M. asterias
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mustelus asterias Cloquet, 1821[2]
| |
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
The starry smooth-hound (Mustelus asterias) is a houndshark of the family Triakidae. It is found on the continental shelves of the northeast Atlantic, between latitudes 61 and 16° N, from the surface to a depth of 200 m (660 ft).
Description
The starry smooth-hound grows to a length of about 140 cm (55 in). It is grey or greyish-brown with a scattering of small white spots on its dorsal (upper) surface and white on its ventral (under) surface. It is a long, lean fish with a somewhat rounded snout and rows of shallowly projecting teeth. The two dorsal fins are of similar shape, but the hindmost one is a little smaller than the foremost. A notch occurs in the upper lobe of the caudal fin and the lower lobe is of medium size.[3]
Distribution and habitat
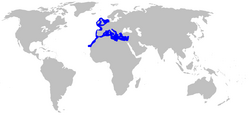
This species of houndshark is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Its range extends from off southern Norway, Scotland, and the North Sea southwards to Algeria, Morocco, and off the Western Sahara. It is found in the whole of the Mediterranean, but not in the Black Sea.[1] It is found on the continental shelf and around islands at depths to at least 200 m (660 ft) and prefers places where the seabed is sand or gravel.[4]
This species of houndshark was found in the Thames River of London in 2021,[5] and Plymouth National Marine Park in April 2022 [6]
Biology
The starry smooth-hound mostly feeds on crustaceans, such as crabs, lobsters, and slipper lobsters, and molluscs. It matures at a length around 80 to 85 cm (31 to 33 in). It is an ovoviviparous fish, retaining its eggs in its oviduct, where the young are nourished by the egg yolk and the oviduct's secretions. Seven to 15 young are in a litter, and they are about 30 cm (12 in) long at birth.[3][4]
Status
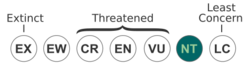
The IUCN, in its Red List of Threatened Species, lists the starry smooth-hound as "near threatened". In the Mediterranean Sea, it is less common and is targeted for human consumption along with the closely related common smooth-hound (Mustelus mustelus).[1] Numbers in the Mediterranean have dwindled and in this region it might qualify for "Vulnerable" status were it not plentiful elsewhere.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Jabado, R.W.; Ellis, J.R.; McCully-Philipps, S.R.; Dulvy, N.K.; Farrell, E.D.; Mancusi, C.; Derrick, D. (2021). "Mustelus asterias". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T39357A124405496. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T39357A124405496.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/39357/124405496. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bailly, Nicolas (2013). "Mustelus asterias Cloquet, 1819". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=105821.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Starry smoothhound (Mustelus asterias)". Fishes of the NE Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Marine Species Information Portal. http://species-identification.org/species.php?species_group=fnam&id=997.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Carpenter, Kent E.. "Mustelus asterias Cloquet, 1819". FishBase. http://www.fishbase.org/summary/Mustelus-asterias.html.
- ↑ "Venomous sharks found in London's Thames river". 10 November 2021. https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/venomous-sharks-london-scli-intl-gbr-scn/index.html.
- ↑ Simpson, Zhara (2022-04-24). "Incredible shark species spotted in Plymouth" (in en). https://www.plymouthherald.co.uk/news/plymouth-news/incredible-shark-species-spotted-plymouths-6990330.
Further reading
- Compagno, Dando, & Fowler, Sharks, Collins Gem, HarperCollins, London (2006) ISBN 0-00-721986-5
Wikidata ☰ Q2419006 entry
 |