Biology:VAMP2
 Generic protein structure example |
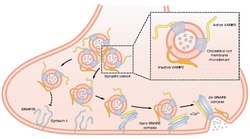
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAMP2 gene.[1][2]
Function
Synaptobrevins/VAMPs, syntaxins, and the 25-kD synaptosomal-associated protein SNAP25 are the main components of a protein complex involved in the docking and/or fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. VAMP2 is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family. VAMP2 is thought to participate in neurotransmitter release at a step between docking and fusion. Mice lacking functional synaptobrevin2/VAMP2 gene cannot survive after birth, and have a dramatically reduced synaptic transmission, around 10% of control.[3] The protein forms a stable complex with syntaxin, synaptosomal-associated protein, 25 kD, and complexin. It also forms a distinct complex with synaptophysin.[2]
Clinical significance
Heterozygous mutations in VAMP2 cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with hypotonia and autistic features (with or without hyperkinetic movements).[4][5][6]
Interactions
VAMP2 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ↑ "Structures and chromosomal localizations of two human genes encoding synaptobrevins 1 and 2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 265 (28): 17267–73. Oct 1990. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)44898-8. PMID 1976629.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Entrez Gene: VAMP2 vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (synaptobrevin 2)". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=6844.
- ↑ "SNARE function analyzed in synaptobrevin/VAMP knockout mice". Science 294 (5544): 1117–22. Nov 2001. doi:10.1126/science.1064335. PMID 11691998. Bibcode: 2001Sci...294.1117S.
- ↑ "Mutations in the Neuronal Vesicular SNARE VAMP2 Affect Synaptic Membrane Fusion and Impair Human Neurodevelopment". The American Journal of Human Genetics 104 (4): 721‐730. Apr 2019. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.02.016. PMID 30929742.
- ↑ "Variant in the neuronal vesicular SNARE VAMP2 (synaptobrevin-2): First report in Japan". Brain and Development 42 (7): 529–533. Apr 2020. doi:10.1016/j.braindev.2020.04.001. PMID 32336483.
- ↑ "OMIM entry: Neurodevelopmental disorder with hypotonia and autistic features with or without hyperkinetic movements". https://www.omim.org/entry/618760.
- ↑ "Isolation and characterization of a dual prenylated Rab and VAMP2 receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 (43): 26991–8. Oct 1997. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.43.26991. PMID 9341137.
- ↑ "Spring, a novel RING finger protein that regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (44): 40824–33. Nov 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106141200. PMID 11524423.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Effect of mutations in vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) on the assembly of multimeric protein complexes". The Journal of Neuroscience 17 (5): 1596–603. Mar 1997. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-05-01596.1997. PMID 9030619.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Three-dimensional structure of the complexin/SNARE complex". Neuron 33 (3): 397–409. Jan 2002. doi:10.1016/s0896-6273(02)00583-4. PMID 11832227. https://epublications.marquette.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1227&context=chem_fac.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Soluble NSF attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) in RBL-2H3 mast cells: functional role of syntaxin 4 in exocytosis and identification of a vesicle-associated membrane protein 8-containing secretory compartment". Journal of Immunology 164 (11): 5850–7. Jun 2000. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5850. PMID 10820264.
- ↑ "Intracellular localisation of SNARE proteins in rat parotid acinar cells: SNARE complexes on the apical plasma membrane". Archives of Oral Biology 48 (8): 597–604. Aug 2003. doi:10.1016/s0003-9969(03)00116-x. PMID 12828989.
- ↑ "Role of SNAP23 in insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mediation of complex formation between syntaxin4 and VAMP2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (11): 8240–7. Mar 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.11.8240. PMID 10713150.
- ↑ "A conformational switch in syntaxin during exocytosis: role of munc18". The EMBO Journal 18 (16): 4372–82. Aug 1999. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.16.4372. PMID 10449403.
- ↑ "Complexins: cytosolic proteins that regulate SNAP receptor function". Cell 83 (1): 111–9. Oct 1995. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90239-2. PMID 7553862.
- ↑ "Munc 18a binding to syntaxin 1A and 1B isoforms defines its localization at the plasma membrane and blocks SNARE assembly in a three-hybrid system assay". Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences 20 (2): 169–80. Jun 2002. doi:10.1006/mcne.2002.1122. PMID 12093152.
- ↑ "A stable interaction between syntaxin 1a and synaptobrevin 2 mediated by their transmembrane domains". FEBS Letters 446 (1): 40–4. Mar 1999. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00028-9. PMID 10100611.
- ↑ "Role of vesicle-associated membrane protein-2, through Q-soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor/R-soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor interaction, in the exocytosis of specific and tertiary granules of human neutrophils". Journal of Immunology 170 (2): 1034–42. Jan 2003. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.170.2.1034. PMID 12517971.
- ↑ "Insulin-responsive tissues contain the core complex protein SNAP-25 (synaptosomal-associated protein 25) A and B isoforms in addition to syntaxin 4 and synaptobrevins 1 and 2". The Biochemical Journal. 317 317 (3): 945–54. Aug 1996. doi:10.1042/bj3170945. PMID 8760387.
- ↑ "Human platelets contain SNARE proteins and a Sec1p homologue that interacts with syntaxin 4 and is phosphorylated after thrombin activation: implications for platelet secretion". Blood 93 (8): 2617–26. Apr 1999. doi:10.1182/blood.V93.8.2617. PMID 10194441.
Further reading
- "Subcellular distribution of docking/fusion proteins in neutrophils, secretory cells with multiple exocytic compartments". Journal of Immunology 155 (12): 5750–9. Dec 1995. PMID 7499863.
- "Transport route for synaptobrevin via a novel pathway of insertion into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane". The EMBO Journal 14 (2): 217–23. Jan 1995. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06994.x. PMID 7835332.
- "SNAP-25, a t-SNARE which binds to both syntaxin and synaptobrevin via domains that may form coiled coils". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 269 (44): 27427–32. Nov 1994. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47003-2. PMID 7961655.
- "A post-docking role for synaptobrevin in synaptic vesicle fusion". Neuron 12 (6): 1269–79. Jun 1994. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(94)90443-X. PMID 8011337.
- "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene 138 (1–2): 171–4. Jan 1994. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- "Insulin-responsive tissues contain the core complex protein SNAP-25 (synaptosomal-associated protein 25) A and B isoforms in addition to syntaxin 4 and synaptobrevins 1 and 2". The Biochemical Journal. 317 317 (3): 945–54. Aug 1996. doi:10.1042/bj3170945. PMID 8760387.
- "Syntaxin-4 is localized to the apical plasma membrane of rat renal collecting duct cells: possible role in aquaporin-2 trafficking". The Journal of Clinical Investigation 98 (4): 906–13. Aug 1996. doi:10.1172/JCI118873. PMID 8770861.
- "Identification of SNAP receptors in rat adipose cell membrane fractions and in SNARE complexes co-immunoprecipitated with epitope-tagged N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein". The Biochemical Journal. 320 320 (2): 429–36. Dec 1996. doi:10.1042/bj3200429. PMID 8973549.
- "Direct interaction of the rat unc-13 homologue Munc13-1 with the N terminus of syntaxin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 (4): 2520–6. Jan 1997. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.4.2520. PMID 8999968.
- "Effect of mutations in vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) on the assembly of multimeric protein complexes". The Journal of Neuroscience 17 (5): 1596–603. Mar 1997. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-05-01596.1997. PMID 9030619.
- "Isolation and characterization of a dual prenylated Rab and VAMP2 receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 272 (43): 26991–8. Oct 1997. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.43.26991. PMID 9341137.
- "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene 200 (1–2): 149–56. Oct 1997. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- "Identification of a human homologue of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)-associated protein of 33 kDa (VAP-33): a broadly expressed protein that binds to VAMP". The Biochemical Journal. 333 333 (2): 247–51. Jul 1998. doi:10.1042/bj3330247. PMID 9657962.
- "A splice-isoform of vesicle-associated membrane protein-1 (VAMP-1) contains a mitochondrial targeting signal". Molecular Biology of the Cell 9 (7): 1649–60. Jul 1998. doi:10.1091/mbc.9.7.1649. PMID 9658161.
- "Syntaxin 13 mediates cycling of plasma membrane proteins via tubulovesicular recycling endosomes". The Journal of Cell Biology 143 (4): 957–71. Nov 1998. doi:10.1083/jcb.143.4.957. PMID 9817754.
- "Molecular cloning and characterization of mammalian homologues of vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated (VAMP-associated) proteins". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 254 (1): 21–6. Jan 1999. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9876. PMID 9920726.
- "Syntaxin 11 is associated with SNAP-23 on late endosomes and the trans-Golgi network". Journal of Cell Science. 112 112 (6): 845–54. Mar 1999. doi:10.1242/jcs.112.6.845. PMID 10036234.
- "A stable interaction between syntaxin 1a and synaptobrevin 2 mediated by their transmembrane domains". FEBS Letters 446 (1): 40–4. Mar 1999. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00028-9. PMID 10100611.
- "Mixed and non-cognate SNARE complexes. Characterization of assembly and biophysical properties". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (22): 15440–6. May 1999. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.22.15440. PMID 10336434.



