Biology:Vesicle-associated membrane protein
From HandWiki
Short description: Protein family
| Synaptobrevin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
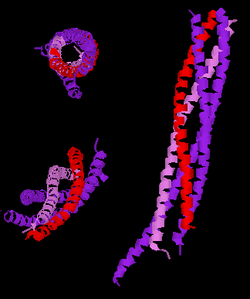 Three different views of the high resolution structure of a truncated neuronal SNARE complex. Legend: synaptobrevin-2 (red), Syntaxin-1 (pink), SNAP-25 (purple). | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Synaptobrevin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00957 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR016444 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00368 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1sfc / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 197 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 4wy4 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 198 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
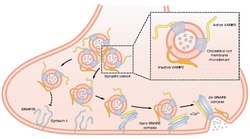
Vesicle associated membrane proteins (VAMPs) are a family of SNARE proteins with similar structure, and are mostly involved in vesicle fusion.
- VAMP1 and VAMP2 proteins known as synaptobrevins are expressed in brain and are constituents of the synaptic vesicles, where they participate in neurotransmitter release.
- VAMP3 (known as cellubrevin) is ubiquitously expressed and participates in regulated and constitutive exocytosis as a constituent of secretory granules and secretory vesicles.
- VAMP5 and VAMP7 participate in constitutive exocytosis.
- VAMP5 is a constituent of secretory vesicles, myotubes and tubulovesicular structures.
- VAMP7 is found both in secretory granules and endosomes.
- VAMP8 (known as endobrevin) participates in endocytosis and is found in early endosomes. VAMP8 also participates the regulated exocytosis in pancreatic acinar cells.
- VAMP4 is involved in transport from the Golgi.[1]
References
- ↑ "Vesicle-associated membrane protein 4 is implicated in trans-Golgi network vesicle trafficking". Mol. Biol. Cell 10 (6): 1957–72. 1999. doi:10.1091/mbc.10.6.1957. PMID 10359608.
External links
- Vesicle-Associated+Membrane+Protein+1 at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |

