Biology:Vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I)
| VOMI | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
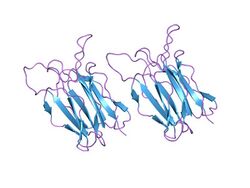 crystal structure of vitelline membrane outer layer protein i (vmo-i): a folding motif with homologous greek key structures related by an internal three-fold symmetry | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | VOMI | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03762 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR005515 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1vmo / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, this entry refers to a protein domain called, the Vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I). It is a structure found on the outside of an egg, in the vitelline membrane.
Function
The major role of the vitelline membrane is to prevent the mixing of the yolk and albumen and also act as an important anti-microbial barrier, as indicated by the high content of lysozyme in the outer layer [1] Vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I) binds tightly to ovomucin fibrils, which construct the backbone of the outer layer membrane. VMO-I has considerable activity to synthesize N-acetylchito-oligosaccharide from N-acetylglucosamine hexasaccharides but no hydrolysis activity. VMO-I is composed of 163 aa[2]
Structure
The structure[3] consists of three beta-sheets forming Greek key motifs, which are related by an internal pseudo three-fold symmetry. Furthermore, the structure of VOMI has strong similarity to the structure of the delta-endotoxin, as well as a carbohydrate-binding site in the top region of the common fold.[4] VMO-I revealed a unique structure of the P-prism fold, a new type of multi-sheet assembly.
References
- ↑ "Exocytosis and proteomic analysis of the vesicle content of granular hemocytes from a crayfish.". Dev Comp Immunol 29 (12): 1017–31. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2005.03.010. PMID 15975654.
- ↑ "Characterization of vitelline membrane outer layer protein I, VMO-I: amino acid sequence and structural stability.". J Biochem 117 (6): 1183–91. 1995. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124842. PMID 7490258. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7490258.
- ↑ "Crystal structure of vitelline membrane outer layer protein I (VMO-I): a folding motif with homologous Greek key structures related by an internal three-fold symmetry". EMBO J. 13 (5): 1003–10. March 1994. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06348.x. PMID 8131734.
- ↑ "The beta-prism: a new folding motif". Trends Biochem. Sci. 21 (1): 3–6. January 1996. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(06)80018-6. PMID 8848836.
 |

