Biology:YecM bacterial protein domain
From HandWiki
| YecM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 structural genyyecn yecmyeyepomics, protein ec4020 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | YecM | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF06185 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0104 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR010393 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1k4n / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, YecM refers to a protein domain found in Escherichia coli. It is a conserved, hypothetical protein with sequence homologues found exclusively in bacteria. Several bacterial YecM proteins in this particular family are of unknown function.
Function
The precise function of the YecM domain remains to be elucidated. However, YecM structural homologues reveal that all the proteins bind a divalent metal cation. This comparison suggests that YecM may be a metal-binding protein and therefore may function as an enzyme.[1]
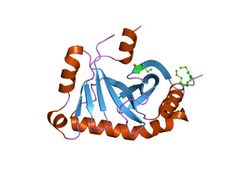
Structure
The protein domain, YecM, is a monomer. The eight, mostly antiparallel beta-strands form around C-terminal alpha-helix. There are four alpha helices in total.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Crystal structure of human Edc3 and its functional implications.". Mol Cell Biol 28 (19): 5965–76. 2008. doi:10.1128/MCB.00761-08. PMID 18678652.
 |

