Catalogue of Triangle Cubics
The Catalogue of Triangle Cubics is an online resource containing detailed information about more than 1200 cubic curves in the plane of a reference triangle.[1] The resource is maintained by Bernard Gibert. Each cubic in the resource is assigned a unique identification number of the form "Knnn" where "nnn" denotes three digits. The identification number of the first entry in the catalogue is "K001" which is the Neuberg cubic of the reference triangle ABC. The catalogue provides, among other things, the following information about each of the cubics listed:
- Barycentric equation of the curve
- A list of triangle centers which lie on the curve
- Special points on the curve which are not triangle centers
- Geometric properties of the curve
- Locus properties of the curve
- Other special properties of the curve
- Other curves related to the cubic curve
- Plenty of neat and tidy figures illustrating the various properties
- References to literature on the curve
The equations of some of the cubics listed in the Catalogue are so incredibly complicated that the maintainer of the website has refrained from putting up the equation in the webpage of the cubic; instead, a link to a file giving the equation in an unformatted text form is provided. For example, the equation of the cubic K1200 is given as a text file.[2]
Coordinates
Suppose that △ABC is a triangle with sidelengths Relative to △ABC, many named cubics pass through well-known points. Examples shown below use two kinds of homogeneous coordinates: trilinear and barycentric.
To convert from trilinear to barycentric in a cubic equation, substitute as follows:
to convert from barycentric to trilinear, use
Many equations for cubics have the form
In the examples below, such equations are written more succinctly in "cyclic sum notation", like this:
- .
The cubics listed below can be defined in terms of the isogonal conjugate, denoted by X*, of a point X not on a sideline of △ABC. A construction of X* follows. Let LA be the reflection of line XA about the internal angle bisector of angle A, and define LB and LC analogously. Then the three reflected lines concur in X*. In trilinear coordinates, if then
First few triangle cubics in the catalogue
The following are the first ten cubics given in the Catalogue.
| Identification number | Name(s) | Equation in barycentric coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| K001 | Neuberg cubic, 21-point cubic, 37-point cubic | |
| K002 | Thomson cubic, 17-point cubic | |
| K003 | McCay cubic, Griffiths cubic | |
| K004 | Darboux cubic | |
| K005 | Napoleon cubic, Feuerbach cubic | |
| K006 | Orthocubic | |
| K007 | Lucas cubic | |
| K008 | Droussent cubic | |
| K009 | Lemoine cubic | |
| K010 | Simson cubic |

Individual curves
Neuberg cubic
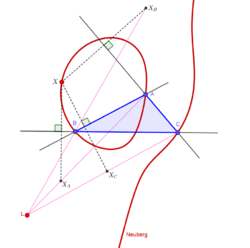
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The Neuberg cubic (named after Joseph Jean Baptiste Neuberg) is the locus of a point X such that X* is on the line EX, where E is the Euler infinity point (X(30) in the Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers). Also, this cubic is the locus of X such that the triangle △XAXBXC is perspective to △ABC, where △XAXBXC is the reflection of X in the lines BC, CA, AB, respectively
The Neuberg cubic passes through the following points: incenter, circumcenter, orthocenter, both Fermat points, both isodynamic points, the Euler infinity point, other triangle centers, the excenters, the reflections of A, B, C in the sidelines of △ABC, and the vertices of the six equilateral triangles erected on the sides of △ABC.
For a graphical representation and extensive list of properties of the Neuberg cubic, see K001 at Berhard Gibert's Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
Thomson cubic
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The Thomson cubic is the locus of a point X such that X* is on the line GX, where G is the centroid.
The Thomson cubic passes through the following points: incenter, centroid, circumcenter, orthocenter, symmedian point, other triangle centers, the vertices A, B, C, the excenters, the midpoints of sides BC, CA, AB, and the midpoints of the altitudes of △ABC. For each point P on the cubic but not on a sideline of △ABC, the isogonal conjugate of P is also on the cubic.
For graphs and properties, see K002 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
Darboux cubic
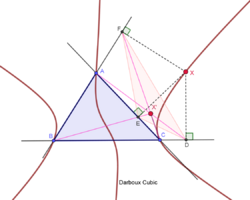
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The Darboux cubic is the locus of a point X such that X* is on the line LX, where L is the de Longchamps point. Also, this cubic is the locus of X such that the pedal triangle of X is the cevian triangle of some point (which lies on the Lucas cubic). Also, this cubic is the locus of a point X such that the pedal triangle of X and the anticevian triangle of X are perspective; the perspector lies on the Thomson cubic.
The Darboux cubic passes through the incenter, circumcenter, orthocenter, de Longchamps point, other triangle centers, the vertices A, B, C, the excenters, and the antipodes of A, B, C on the circumcircle. For each point P on the cubic but not on a sideline of △ABC, the isogonal conjugate of P is also on the cubic.
For graphics and properties, see K004 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
Napoleon–Feuerbach cubic
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The Napoleon–Feuerbach cubic is the locus of a point X* is on the line NX, where N is the nine-point center, (N = X(5) in the Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers).
The Napoleon–Feuerbach cubic passes through the incenter, circumcenter, orthocenter, 1st and 2nd Napoleon points, other triangle centers, the vertices A, B, C, the excenters, the projections of the centroid on the altitudes, and the centers of the 6 equilateral triangles erected on the sides of △ABC.
For a graphics and properties, see K005 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
Lucas cubic
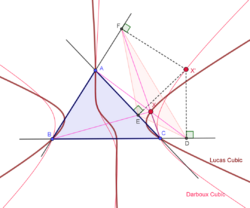
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The Lucas cubic is the locus of a point X such that the cevian triangle of X is the pedal triangle of some point; the point lies on the Darboux cubic.
The Lucas cubic passes through the centroid, orthocenter, Gergonne point, Nagel point, de Longchamps point, other triangle centers, the vertices of the anticomplementary triangle, and the foci of the Steiner circumellipse.
For graphics and properties, see K007 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
1st Brocard cubic
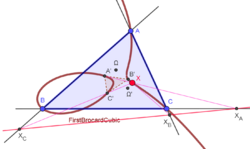
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
Let △A'B'C' be the 1st Brocard triangle. For arbitrary point X, let XA, XB, XC be the intersections of the lines XA′, XB′, XC′ with the sidelines BC, CA, AB, respectively. The 1st Brocard cubic is the locus of X for which the points XA, XB, XC are collinear.
The 1st Brocard cubic passes through the centroid, symmedian point, Steiner point, other triangle centers, and the vertices of the 1st and 3rd Brocard triangles.
For graphics and properties, see K017 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
2nd Brocard cubic
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The 2nd Brocard cubic is the locus of a point X for which the pole of the line XX* in the circumconic through X and X* lies on the line of the circumcenter and the symmedian point (i.e., the Brocard axis). The cubic passes through the centroid, symmedian point, both Fermat points, both isodynamic points, the Parry point, other triangle centers, and the vertices of the 2nd and 4th Brocard triangles.
For a graphics and properties, see K018 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
1st equal areas cubic
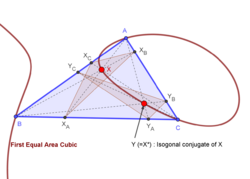
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
The 1st equal areas cubic is the locus of a point X such that area of the cevian triangle of X equals the area of the cevian triangle of X*. Also, this cubic is the locus of X for which X* is on the line S*X, where S is the Steiner point. (S = X(99) in the Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers).
The 1st equal areas cubic passes through the incenter, Steiner point, other triangle centers, the 1st and 2nd Brocard points, and the excenters.
For a graphics and properties, see K021 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
2nd equal areas cubic
Trilinear equation:
Barycentric equation:
For any point (trilinears), let and The 2nd equal areas cubic is the locus of X such that the area of the cevian triangle of XY equals the area of the cevian triangle of XZ.
The 2nd equal areas cubic passes through the incenter, centroid, symmedian point, and points in Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers indexed as X(31), X(105), X(238), X(292), X(365), X(672), X(1453), X(1931), X(2053), and others.
For a graphics and properties, see K155 at Cubics in the Triangle Plane.
GeoGebra tool to draw triangle cubics

GeoGebra, the software package for interactive geometry, algebra, statistics and calculus application has a built-in tool for drawing the cubics listed in the Catalogue.[3] The command
- Cubic( <Point>, <Point>, <Point>, n)
prints the n-th cubic in the Catalogue for the triangle whose vertices are the three points listed. For example, to print the Thomson cubic of the triangle whose vertices are A, B, C the following command may be issued:
- Cubic(A, B, C, 2)
See also
References
- ↑ Bernard Gibert. "Catalogue of Triangle Cubics". Bernard Gibert. http://bernard-gibert.fr/.
- ↑ "K1200: a crunodal KHO-cubic". Bernard Gibert. https://bernard-gibert.pagesperso-orange.fr/Exemples/k1200.html.
- ↑ "Cubic Command". GeoGebra. https://wiki.geogebra.org/en/Cubic_Command.
 |
