Champernowne constant
In mathematics, the Champernowne constant C10 is a transcendental real constant whose decimal expansion has important properties. It is named after economist and mathematician D. G. Champernowne, who published it as an undergraduate in 1933.[1] The number is defined by concatenating the base 10 representations of the positive integers:
Champernowne constants can also be constructed in other bases similarly; for example,
- C2 = 0.11011100101110111... 2
and
- C3 = 0.12101112202122... 3.
The Champernowne word or Barbier word is the sequence of digits of C10 obtained by writing it in base 10 and juxtaposing the digits:[2][3]
More generally, a Champernowne sequence (sometimes also called a Champernowne word) is any sequence of digits obtained by concatenating all finite digit-strings (in any given base) in some recursive order.[4] For instance, the binary Champernowne sequence in shortlex order is
where spaces (otherwise to be ignored) have been inserted just to show the strings being concatenated.
Properties
A real number x is said to be normal if its digits in every base follow a uniform distribution: all digits being equally likely, all pairs of digits equally likely, all triplets of digits equally likely, etc. A number x is said to be normal in base b if its digits in base b follow a uniform distribution.
If we denote a digit string as [a0, a1, ...], then, in base 10, we would expect strings [0], [1], [2], …, [9] to occur 1/10 of the time, strings [0,0], [0,1], ..., [9,8], [9,9] to occur 1/100 of the time, and so on, in a normal number.
Champernowne proved that [math]\displaystyle{ C_{10} }[/math] is normal in base 10,[1] while Nakai and Shiokawa proved a more general theorem, a corollary of which is that [math]\displaystyle{ C_{b} }[/math] is normal in base [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] for any b.[5] It is an open problem whether [math]\displaystyle{ C_{k} }[/math] is normal in bases [math]\displaystyle{ b \neq k }[/math].
Kurt Mahler showed that the constant is transcendental.[6] The irrationality measure of [math]\displaystyle{ C_{10} }[/math] is [math]\displaystyle{ \mu(C_{10})=10 }[/math], and more generally [math]\displaystyle{ \mu(C_b)=b }[/math] for any base [math]\displaystyle{ b\ge 2 }[/math].[7]
The Champernowne word is a disjunctive sequence.
Series
The definition of the Champernowne constant immediately gives rise to an infinite series representation involving a double sum, [math]\displaystyle{ C_{10}=\sum_{n=1}^\infty 10^{-\delta_{10}(n)} \sum_{k=10^{n-1}}^{10^n-1}\frac{k}{10^{n(k-10^{n-1}+1)}}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_{10}(n)= 9\sum_{\ell=1}^{n-1}10^{\ell-1}\ell }[/math] is the number of digits between the decimal point and the first contribution from an n-digit base-10 number; these expressions generalize to an arbitrary base b by replacing 10 and 9 with b and b − 1 respectively. Alternative forms are [math]\displaystyle{ C_b=\sum_{n=1}^\infty n \cdot b^{-\left(\sum\limits_{k=1}^n\left\lceil\log_{b}(k+1)\right\rceil\right)} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ C_b=\sum_{n=1}^\infty n \cdot b^{-\left(n+\sum\limits_{k=1}^{n-1}\left\lfloor\log_b(k+1)\right\rfloor\right)}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \lfloor x \rfloor }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \lceil x \rceil }[/math] denote the floor and ceiling functions.[8][9]
Returning to the first of these series, both the summand of the outer sum and the expression for [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_b(n) }[/math] can be simplified using the closed form for the two-dimensional geometric series: [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{k=n}^\infty ka^k=a^n\frac{n-(n-1)a}{(1-a)^2}. }[/math]
The resulting expression for [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_b(n) }[/math] is [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_b(n) = (b-1)\sum_{\ell=1}^{n-1}b^{\ell-1}\ell = \frac{1}{b-1}\left(1+b^{n-1}((b-1)n-b)\right), }[/math] while the summand of the outer sum becomes [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align}b^{-\delta_b(n)} \sum_{k=b^{n-1}}^{b^n-1}\frac{k}{b^{n(k-b^{n-1}+1)}} &= b^{-\delta_b(n)}b^{n(b^{n-1}-1)}\left(\sum_{k=b^{n-1}}^\infty\frac{k}{b^{nk}}-\sum_{k=b^n}^\infty\frac{k}{b^{nk}}\right)\\ &= \frac{b^{2n-1}-b^{n-1}+1}{\left(b^n-1\right)^2}b^{-\delta_b(n)}-\frac{b^{2n}-b^n+1}{\left(b^n-1\right)^2}b^{-\delta_b(n+1)}.\end{align} }[/math] Summing over all n ≥ 1 gives [math]\displaystyle{ C_b = \frac{b}{(b-1)^2}-\sum_{n=1}^\infty \left(\frac{b^{2n}-b^n+1}{\left(b^n-1\right)^2} - \frac{b^{2n+1}-b^n+1}{\left(b^{n+1}-1\right)^2}\right)b^{-\delta_b(n+1)}. }[/math] Observe that in the summand, the expression in parentheses is approximately [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{b-1}{b} }[/math] for n ≥ 2 and rapidly approaches that value as n grows, while the exponent [math]\displaystyle{ \delta_b(n+1) }[/math] grows exponentially with n. As a consequence, each additional term provides an exponentially growing number of correct digits even though the number of digits in the numerators and denominators of the fractions comprising these terms grows only linearly. For example, the first few terms of C10 are [math]\displaystyle{ C_{10} = \frac{10}{81} - \left[\left(\frac{91}{81}-\frac{991}{9801}\right)\times10^{-9}+\left(\frac{9901}{9801}-\frac{99901}{998001}\right)\times10^{-189}+\left(\frac{999001}{998001}-\frac{9999001}{99980001}\right)\times10^{-2889}+\ldots\right]. }[/math]
Continued fraction expansion
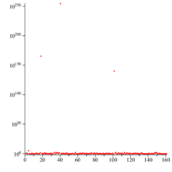
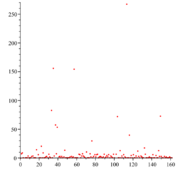
The simple continued fraction expansion of Champernowne's constant does not terminate (because the constant is not rational) and is aperiodic (because it is not an irreducible quadratic). It exhibits extremely large terms appearing between many small ones. For example, in base 10,
- C10 = [0; 8, 9, 1, 149083, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 3, 4, 1, 1, 1, 15, 4 57540 11139 10310 76483 64662 82429 56118 59960 39397 10457 55500 06620 04393 09026 26592 56314 93795 32077 47128 65631 38641 20937 55035 52094 60718 30899 84575 80146 98631 48833 59214 17830 10987, 6, 1, 1, ...]. (sequence A030167 in the OEIS)
The large number at position 18 has 166 digits, and the next very large term at position 40 of the continued fraction has 2504 digits. That there are such large numbers as terms of the continued fraction expansion means that the convergents obtained by stopping before these large numbers provide an exceptionally good approximation of the Champernowne constant. For example, truncating just before the 4th partial quotient, gives [math]\displaystyle{ 10/81 = \sum_{k=1}^\infty k/10^k = 0.\overline{123456790}, }[/math] which matches the first term in the rapidly converging series expansion of the previous section and which approximates Champernowne's constant with an error of about 1 × 10−9. Truncating just before the 18th partial quotient gives an approximation that matches the first two terms of the series, that is, the terms up to the term containing 10−9, [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \frac{60499999499}{490050000000} &= 0.123456789+10^{-9}\sum_{k=10}^\infty k/10^{2(k-9)}=0.123456789+10^{-9}\frac{991}{9801}\\ &= 0.123456789\overline{10111213141516171819\ldots90919293949596979900010203040506070809}, \end{align} }[/math] which approximates Champernowne's constant with error approximately 9 × 10−190.
The first and second incrementally largest terms ("high-water marks") after the initial zero are 8 and 9, respectively, and occur at positions 1 and 2. Sikora (2012) noticed that the number of digits in the high-water marks starting with the fourth display an apparent pattern.[10] Indeed, the high-water marks themselves grow doubly-exponentially, and the number of digits [math]\displaystyle{ d_n }[/math] in the nth mark for [math]\displaystyle{ n\geqslant 3 }[/math] are
- 6, 166, 2504, 33102, 411100, 4911098, 57111096, 651111094, 7311111092, ...
whose pattern becomes obvious starting with the 6th high-water mark. The number of terms can be given by [math]\displaystyle{ d_n=\frac{13-67 \times 10^{n-3}}{45}+\left(2^n5^{n-3}-2\right),n\in\mathbb{Z}\cap\left[3,\infty\right). }[/math]
However, it is still unknown as to whether or not there is a way to determine where the large terms (with at least 6 digits) occur, or their values. The high-water marks themselves are located at positions
See also
- Copeland–Erdős constant, a similar normal number, defined using the prime numbers
- Liouville's constant, another constant defined by its decimal representation
- Smarandache–Wellin number, another number obtained through concatenation a representation in a given base.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Champernowne 1933
- ↑ Cassaigne & Nicolas (2010) p.165
- ↑ Allouche, Jean-Paul; Shallit, Jeffrey (2003). Automatic Sequences: Theory, Applications, Generalizations. Cambridge University Press. p. 299. ISBN 978-0-521-82332-6.
- ↑ Disjunctive sequences: An overview, University of Auckland, New Zealand, 1997, pp. 1–35
- ↑ Nakai & Shiokawa 1992
- ↑ K. Mahler, Arithmetische Eigenschaften einer Klasse von Dezimalbrüchen, Proc. Konin. Neder. Akad. Wet. Ser. A. 40 (1937), p. 421–428.
- ↑ Masaaki Amou, Approximation to certain transcendental decimal fractions by algebraic numbers, Journal of Number Theory, Volume 37, Issue 2, February 1991, Pages 231–241
- ↑ John K. Sikora: Analysis of the High Water Mark Convergents of Champernowne's Constant in Various Bases, in: arXiv:1408.0261, 1 Aug 2014, see Definition 9
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Champernowne constant". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ChampernowneConstant.html.
- ↑ Sikora, J. K. "On the High Water Mark Convergents of Champernowne's Constant in Base Ten." 3 Oct 2012. http://arxiv.org/abs/1210.1263
- Cassaigne, J.; Nicolas, F. (2010). "Factor complexity". in Berthé, Valérie; Rigo, Michel. Combinatorics, automata, and number theory. Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications. 135. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 163–247. ISBN 978-0-521-51597-9.
- "The construction of decimals normal in the scale of ten", Journal of the London Mathematical Society 8 (4): 254–260, 1933, doi:10.1112/jlms/s1-8.4.254.
- Nakai, Y.; Shiokawa, I. (1992), "Discrepancy estimates for a class of normal numbers", Acta Arithmetica 62 (3): 271–284, doi:10.4064/aa-62-3-271-284.
 |