Cheap talk
In game theory, cheap talk is a communication framework between players where messages do not directly affect the payoffs of the game. Providing and receiving information is free. This is in contrast to signalling, in which sending certain messages may be costly for the sender depending on the state of the world.
This basic setting set by Vincent Crawford and Joel Sobel[1] has given rise to a variety of variants.
To give a formal definition, cheap talk is communication that is:[2]
- costless to transmit and receive
- non-binding (i.e. does not limit strategic choices by either party)
- unverifiable (i.e. cannot be verified by a third party like a court)
Therefore, an agent engaging in cheap talk could lie with impunity, but may choose in equilibrium not to do so.
Applications
Game theory
Cheap talk can, in general, be added to any game and has the potential to enhance the set of possible equilibrium outcomes. For example, one can add a round of cheap talk in the beginning of the game Battle of the Sexes, a game in which each player announces whether they intend to go to the football game, or the opera. Because the Battle of the Sexes is a coordination game, this initial round of communication may enable the players to select among multiple equilibria, thereby achieving higher payoffs than in the uncoordinated case. The messages and strategies which yield this outcome are symmetric for each player. One strategy is to announce opera or football with even probability; another is to listen to whether a person announces opera (or football), and on hearing this message say opera (or football) as well.[3] If both players announce different options, then no coordination is achieved. In the case of only one player messaging, this could also give that player a first-mover advantage.
It is not guaranteed, however, that cheap talk will have an effect on equilibrium payoffs. Another game, the Prisoner's Dilemma, is a game whose only equilibrium is in dominant strategies. Any pre-play cheap talk will be ignored and players will play their dominant strategies (Defect, Defect) regardless of the messages sent.
Biological applications
It has been commonly argued that cheap talk will have no effect on the underlying structure of the game. In biology authors have often argued that costly signalling best explains signalling between animals (see Handicap principle, Signalling theory). This general belief has been receiving some challenges (see work by Carl Bergstrom[4] and Brian Skyrms 2002, 2004). In particular, several models using evolutionary game theory indicate that cheap talk can have effects on the evolutionary dynamics of particular games.
Crawford and Sobel's definition
Setting
In the basic form of the game, there are two players communicating, one sender S and one receiver R.
Type
Sender S gets knowledge of the state of the world or of his "type" t. Receiver R does not know t ; he has only ex-ante beliefs about it, and relies on a message from S to possibly improve the accuracy of his beliefs.
Message
S decides to send message m. Message m may disclose full information, but it may also give limited, blurred information: it will typically say "The state of the world is between t1 and t2". It may give no information at all.
The form of the message does not matter, as long as there is mutual understanding, common interpretation. It could be a general statement from a central bank's chairman, a political speech in any language, etc. Whatever the form, it is eventually taken to mean "The state of the world is between t1 and t2".
Action
Receiver R receives message m. R updates his beliefs about the state of the world given new information that he might get, using Bayes's rule. R decides to take action a. This action impacts both his own utility and the sender's utility.
Utility
The decision of S regarding the content of m is based on maximizing his utility, given what he expects R to do. Utility is a way to quantify satisfaction or wishes. It can be financial profits, or non-financial satisfaction—for instance the extent to which the environment is protected. → Quadratic utilities: The respective utilities of S and R can be specified by the following:
The theory applies to more general forms of utility, but quadratic preferences makes exposition easier. Thus S and R have different objectives if b ≠ 0. Parameter b is interpreted as conflict of interest between the two players, or alternatively as bias.UR is maximized when a = t, meaning that the receiver wants to take action that matches the state of the world, which he does not know in general. US is maximized when a = t + b, meaning that S wants a slightly higher action to be taken, if b > 0. Since S does not control action, S must obtain the desired action by choosing what information to reveal. Each player's utility depends on the state of the world and on both players' decisions that eventually lead to action a.
Nash equilibrium
We look for an equilibrium where each player decides optimally, assuming that the other player also decides optimally. Players are rational, although R has only limited information. Expectations get realized, and there is no incentive to deviate from this situation.
Theorem

Crawford and Sobel characterize possible Nash equilibria.
- There are typically multiple equilibria, but in a finite number.
- Separating, which means full information revelation, is not a Nash equilibrium.
- Babbling, which means no information transmitted, is always an equilibrium outcome.
When interests are aligned, then information is fully disclosed. When conflict of interest is very large, all information is kept hidden. These are extreme cases. The model allowing for more subtle case when interests are close, but different and in these cases optimal behavior leads to some but not all information being disclosed, leading to various kinds of carefully worded sentences that we may observe.
More generally:
- There exists N* > 0 such that for all N with 1 ≤ N ≤ N*,
- there exists at least an equilibrium in which the set of induced actions has cardinality N; and moreover
- there is no equilibrium that induces more than N* actions.
Messages
While messages could ex-ante assume an infinite number of possible values μ(t) for the infinite number of possible states of the world t, actually they may take only a finite number of values (m1, m2, . . . , mN).
Thus an equilibrium may be characterized by a partition (t0(N), t1(N). . . tN(N)) of the set of types [0, 1], where 0 = t0(N) < t1(N) < . . . < tN(N) = 1. This partition is shown on the top right segment of Figure 1.
The ti(N)'s are the bounds of intervals where the messages are constant: for ti-1(N) < t < ti(N), μ(t) = mi.
Actions
Since actions are functions of messages, actions are also constant over these intervals: for ti-1(N) < t < ti(N), α(t) = α(mi) = ai.
The action function is now indirectly characterized by the fact that each value ai optimizes return for the R, knowing that t is between t1 and t2. Mathematically (assuming that t is uniformly distributed over [0, 1]),
→ Quadratic utilities:
Given that R knows that t is between ti-1 and ti, and in the special case quadratic utility where R wants action a to be as close to t as possible, we can show that quite intuitively the optimal action is the middle of the interval:
Indifference condition
At t = ti, The sender has to be indifferent between sending either message mi-1 or mi. 1 ≤ i≤ N-1
This gives information about N and the ti.
→ Practically: We consider a partition of size N. One can show that
N must be small enough so that the numerator is positive. This determines the maximum allowed value where is the ceiling of , i.e. the smallest positive integer greater or equal to . Example: We assume that b = 1/20. Then N* = 3. We now describe all the equilibria for N=1, 2, or 3 (see Figure 2).
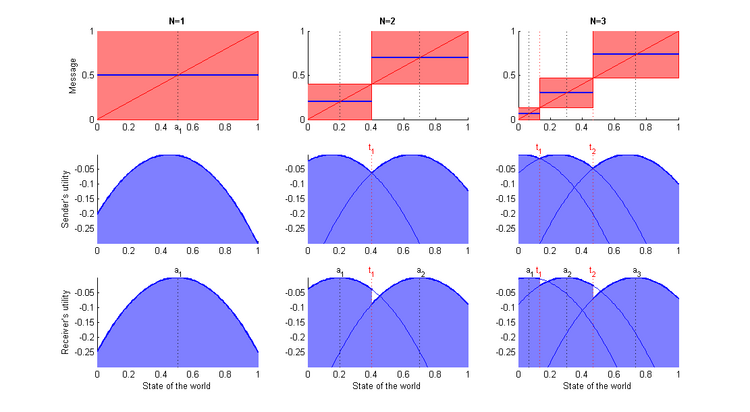
N = 1: This is the babbling equilibrium. t0 = 0, t1 = 1; a1 = 1/2 = 0.5.
N = 2: t0 = 0, t1 = 2/5 = 0.4, t2 = 1; a1 = 1/5 = 0.2, a2 = 7/10 = 0.7.
N = N* = 3: t0 = 0, t1 = 2/15, t2 = 7/15, t3 = 1; a1 = 1/15, a2 = 3/10 = 0.3, a3 = 11/15.
With N = 1, we get the coarsest possible message, which does not give any information. So everything is red on the top left panel. With N = 3, the message is finer. However, it remains quite coarse compared to full revelation, which would be the 45° line, but which is not a Nash equilibrium.
With a higher N, and a finer message, the blue area is more important. This implies higher utility. Disclosing more information benefits both parties.
See also
- Costly signaling theory in evolutionary psychology
- Game theory
- Handicap principle
- Screening game
- Signaling game
Notes
- ↑ Crawford, Vincent P.; Sobel, Joel (November 1982). "Strategic Information Transmission". Econometrica 50 (6): 1431–1451. doi:10.2307/1913390.
- ↑ Farrell, Joseph (1987). "Cheap Talk, Coordination, and Entry". The RAND Journal of Economics 18 (1): 34–39.
- ↑ Farrell and Rabin, 1996
- ↑ "The Biology of Information.". http://octavia.zoology.washington.edu/information_overview.html.
References
- Crawford, V. P.; Sobel, J. (1982). "Strategic Information Transmission". Econometrica 50 (6): 1431–1451. doi:10.2307/1913390.
- Farrell, J.; Rabin, M. (1996). "Cheap Talk". Journal of Economic Perspectives 10 (3): 103–118. doi:10.1257/jep.10.3.103.
- Robson, A. J. (1990). "Efficiency in Evolutionary Games: Darwin, Nash, and the Secret Handshake". Journal of Theoretical Biology 144 (3): 379–396. doi:10.1016/S0022-5193(05)80082-7. PMID 2395377. Bibcode: 1990JThBi.144..379R. http://www.dklevine.com/archive/refs4540.pdf.
- Skyrms, B. (2002). "Signals, Evolution and the Explanatory Power of Transient Information". Philosophy of Science 69 (3): 407–428. doi:10.1086/342451. http://www.dklevine.com/archive/refs4391749000000000001.pdf.
- Skyrms, B. (2004). The Stag Hunt and the Evolution of Social Structure. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82651-9.
 |
