Chemistry:1,1,6-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
From HandWiki
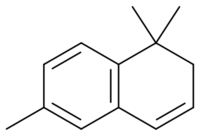
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,1,6-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene
| |
| Other names
1,2-Dihydro-1,1,6-trimethylnaphthalene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TDN |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H16 | |
| Molar mass | 172.271 g·mol−1 |
| Boiling point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K) at 18 Torr[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,1,6-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (TDN) is an aroma compound present in wine,[1] particularly aged Rieslings.[2][3] Chemically, it is classified as a 13C-norisoprenoid, as it has thirteen carbon atoms, and is derived from an isoprenoid by the loss of methylene groups.[4]
In wines, TDN is generally considered to contribute to a desirable aroma in low concentrations, but an undesirable aroma in higher concentrations.[5] The aroma is commonly described as a petrol note or by the French term goût de pétrole.[6]
TDN is believed to be a degradation product of β-carotene and lutein.[4] TDN can also by synthesized in the laboratory from either of the ionones, α-ionone or β-ionone.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Dobrydnev, Alexey; Tarasov, Andrii; Müller, Nikolaus; Volovenko, Yulian; Rauhut, Doris; Jung, Rainer (2020). "An optimized method for synthesis and purification of 1,1,6-trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (TDN)". MethodsX 7: 56–61. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2019.12.009. PMID 31908985.
- ↑ Sacks, Gavin L.; Gates, Matthew J.; Ferry, Francois X.; Lavin, Edward H.; Kurtz, Anne J.; Acree, Terry E. (2012). "Sensory Threshold of 1,1,6-Trimethyl-1,2-dihydronaphthalene (TDN) and Concentrations in Young Riesling and Non-Riesling Wines". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 60 (12): 2998–3004. doi:10.1021/jf205203b. PMID 22397689.
- ↑ Dein, Melissa; Kerley, Trenton; Munafo, John P. (2021). "Characterization of Odorants in a 10-Year-Old Riesling Wine". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 69 (38): 11372–11381. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04196. PMID 34547201.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Waterhouse Lab (2016). "TDN, (1,1,6,-trimethyl-1,2-dihydronapthalene)". University of California, Davis. https://waterhouse.ucdavis.edu/whats-in-wine/tdn-116-trimethyl-12-dihydronapthalene.
- ↑ "Aged Riesling and the development of TDN". The Australian Wine Research Institute. 2012. https://www.awri.com.au/wp-content/uploads/Sept-Oct-2012-AWRI-Report.pdf.
- ↑ Owen Bird (2005). Rheingold - The German Wine Renaissance. Arima Publishing. pp. 90–97. ISBN 978-1-84549-079-9.
 |

