Chemistry:2,3-Dichlorobutadiene
From HandWiki
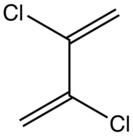
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dichlorobuta-1,3-diene | |
| Other names
2,3-Dichloro-1,3-butadiene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4Cl2 | |
| Molar mass | 122.98 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.1829 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 98 °C (208 °F; 371 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H301, H302, H304, H315, H319, H330, H335, H411 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+310, P301+312, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P320, P321, P330 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2,3-Dichlorobutadiene is a chlorinated derivative of butadiene. This colorless liquid is prone to polymerization, more so than 2-chlorobutadiene. It is used to produce specialized neoprene rubbers.
It can be prepared by the copper-catalyzed isomerization of dichlorobutynes. Alternatively dehydrochlorination of 2,3,4-trichloro-1-butene:[1]
- CH2=C(Cl)CH(Cl)CH2Cl + NaOH → CH2=C(Cl)C(Cl)=CH2 + NaCl + H2O
2,3-Dichlorobutadiene is a precursor to 2,3-diarylbutadienes.[2]
References
- ↑ M. Rossberg (2006). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_233.pub2.
- ↑ Yamamoto Takakazu; Yasuda Takuma; Kobayashi Kazuaki et al. (2006). "Utilization of Industrially Available 2,3-Dichloro-1,3-butadiene for Direct Synthesis of 2,3-Diaryl-1,3-butadienes". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 79 (3): 498–500. doi:10.1246/bcsj.79.498.
 |

