Chemistry:2,5-Furandicarboxaldehyde
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Furan-2,5-dicarboxaldehyde,
2,5-Diformylfuran
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | FDC |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4O3 | |
| Molar mass | 124.095 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
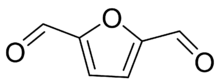
2,5-Furandicarboxaldehyde (FDC) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H2O(CHO)2. It consists of a furan ring with aldehyde groups on the 2 and 5 position. It is therefore classified as a dialdehyde.
Synthesis
2,5-Furandicarboxaldehyde is an oxidation product of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF), which in turn can be prepared from fructose. Alternatively, methods have been developed to convert fructose in one step to 2,5-furandicarboxaldehyde.[1] The conversion from fructose to HMF and FDC can be performed relatively efficiently and following the principles of green chemistry. As such, these materials are often considered as "greener" bio-based alternatives.[citation needed]
Applications
2,5-Furandicarboxaldehyde can be used in the preparation of polyimine vitrimers.[2] It can also be applied as an alternative to glutaraldehyde as crosslinking agent for covalent enzyme immobilisation.[3]
See also
- Terephthalaldehyde (TA)
- 2,5-Furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA)
References
- ↑ Zhou, C.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Song, Y.; Wan, X.; Lin, H.; Yang, Y. (2019). "One-Step Approach to 2,5-Diformylfuran from Fructose over Molybdenum Oxides Supported on Carbon Spheres". ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 7 (1): 315–323. doi:10.1039/c6py01395c.
- ↑ Dhers, S.; Vantomme, G.; Avérous, L. (2019). "A fully bio-based polyimine vitrimer derived from fructose". Green Chemistry 12 (7): 35676–35684. doi:10.1039/C9GC00540D. https://pure.tue.nl/ws/files/129613047/c9gc00540d.pdf.
- ↑ Danielli, C.; Van Langen, L.; Boes, D.; Asora, F.; Anselmi, S.; Provenza, F.; Renzi, M.; Gardossi, L. (2022). "2,5-Furandicarboxaldehyde as a bio-based crosslinking agent replacing glutaraldehyde for covalent enzyme immobilization". RSC Adv. 21 (7): 1596–1601. doi:10.1039/D2RA07153C. PMID 36545099. Bibcode: 2022RSCAd..1235676D.
 |

