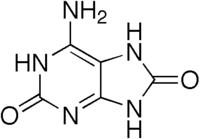
Chemistry:2,8-Dihydroxyadenine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Amino-1H-purine-2,8(7H,9H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 2,8-dihydroxyadenine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5N5O2 | |
| Molar mass | 167.126 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,8-Dihydroxyadenine is a derivative of adenine which accumulates in 2,8 dihydroxy-adenine urolithiasis. The poorly soluble purine 2,8-dihydroxyadenine is excreted in the urine because of a deficiency in the adenine salvage enzyme adenine phosphoribosyltransferase. The defect is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait; the homozygous state is associated with high urinary levels of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine and with crystalluria, calculus formation, and potential nephrotoxicity. The condition primarily presents as renal obstructive disease, but some patients have presented with advanced kidney failure. Allopurinol therapy appears to be effective. 2, 8-dihydroxyadenine formation can be easily controlled with allopurinol, which is administered in a dose of 300 mg/day in adults (10 mg/kg/day in children) in the absence of kidney failure.[1]
References
- Diculescu, VC; Piedade, JA; Oliveira-Brett, AM (2007). "Electrochemical behaviour of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine at a glassy carbon electrode". Bioelectrochemistry 70 (1): 141–6. doi:10.1016/j.bioelechem.2006.03.015. PMID 16713382.
- "Identification of two novel mutations in adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene in patients with 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis". Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 23 (8–9): 1141–5. 2004. doi:10.1081/NCN-200027393. PMID 15571218.
- "2,8-Dihydroxyadenine renal stones in a 41-year-old man". Ann Clin Biochem 41 (Pt 2): 160–1. 2004. doi:10.1258/000456304322880087. PMID 15025810.
 |

