Chemistry:Acetyleugenol
From HandWiki
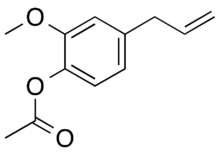
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2-methoxy-4-prop-2-enylphenyl) acetate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 206.241 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Methoxyeugenol Methyleugenol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Acetyleugenol is a phenylpropanoid compound found in cloves. It is the second in abundance to the related compound eugenol in certain extract preparations.[1][2] Like eugenol, its found in several plants such as Acacia nilotica and Piper betle[3][4][5] and has similar antibacterial and antifungal properties on C. albicans and S. mutans.[6] It inhibits aggregation of platelets and has partial agonistic activity on AhR.[2][7][8]
Uses
Acetyleugenol has characteristic odor reminiscent of cloves and thus used as fragrance.[9][10]
See also
- Methyleugenol
References
- ↑ Nassar, Mahmoud; Gaara, Ahmed; El-Ghorab, A.; Farrag, Abdel Razik; Shen, Hui; Huq, Enamul; Mabry, Tom. "Chemical constituents of clove (Syzygium aromaticum, Fam. Myrtaceae) and their antioxidant activity". Latinoam. Quim. 35.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Acetyl eugenol, a component of oil of cloves (Syzygium aromaticum L.) inhibits aggregation and alters arachidonic acid metabolism in human blood platelets". Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 42 (1): 73–81. January 1991. doi:10.1016/0952-3278(91)90070-l. PMID 2011614.
- ↑ "Effect of different extraction techniques on total phenolic and flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity of betelvine and quantification of its phenolic constituents by validated HPTLC method". 3 Biotech 9 (1): 37. January 2019. doi:10.1007/s13205-018-1565-8. PMID 30622875.
- ↑ "Variation in essential oil composition of Rydingia michauxii at the three developmental stages". Natural Product Research 35 (2): 342–345. January 2021. doi:10.1080/14786419.2019.1622112. PMID 31140321. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/8197898.
- ↑ "Efficacy of chemically characterized Piper betle L. essential oil against fungal and aflatoxin contamination of some edible commodities and its antioxidant activity". International Journal of Food Microbiology 142 (1–2): 114–9. August 2010. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.06.011. PMID 20621374.
- ↑ "Antifungal potential of eugenyl acetate against clinical isolates of Candida species". Microbial Pathogenesis 99: 19–29. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2016.07.012. PMID 27452957.
- ↑ "Antiplatelet principles from a food spice clove (Syzygium aromaticum L) [corrected]". Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 48 (5): 363–72. May 1993. doi:10.1016/0952-3278(93)90116-e. PMID 8321872.
- ↑ "Essential oils of culinary herbs and spices display agonist and antagonist activities at human aryl hydrocarbon receptor AhR". Food and Chemical Toxicology 111: 374–384. January 2018. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.049. PMID 29191726.
- ↑ "The Good Scents Company - Aromatic/Hydrocarbon/Inorganic Ingredients Catalog information". http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com/data/rw1005011.html.
- ↑ "RIFM fragrance ingredient safety assessment, eugenyl acetate, CAS Registry Number 93-28-7". Food and Chemical Toxicology 144 (Suppl 1): 111630. October 2020. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111630. PMID 32771453.
 |
