Chemistry:Amarogentin
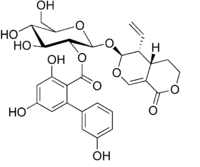 Chemical structure of amarogentin
| |
 Chemical structure of amarogentin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4aS,5R,6S)-5-Ethenyl-1-oxo-4,4a,5,6-tetrahydro-1H,3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-6-yl β-D-glucopyranoside 2-(3,3′,5-trihydroxy[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(4aS,5R,6S)-5-Ethenyl-1-oxo-4,4a,5,6-tetrahydro-1H,3H-pyrano[3,4-c]pyran-6-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl 3,3′,5-trihydroxy[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H30O13 | |
| Molar mass | 586.546 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Amarogentin is a chemical compound found in gentian (Gentiana lutea) or in Swertia chirata.[1]
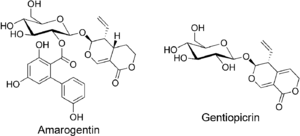
Gentian root has a long history of use as a herbal bitter in the treatment of digestive disorders and is an ingredient of many proprietary medicines. The bitter principles of gentian root are secoiridoid glycosides amarogentin and gentiopicrin. The former is one of the most bitter natural compounds known[2] and is used as a scientific basis for measuring bitterness. In humans, it activates the bitter taste receptor TAS2R50.[3] The biphenylcarboxylic acid moiety is biosynthesized by a polyketide-type pathway, with three units of acetyl-CoA and one unit of 3-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA, this being formed from an early shikimate pathway intermediate and not via cinnamic or benzoic acid.[4]
It also shows an antileishmanial activity in animal models[5] being an inhibitor of topoisomerase I.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Keil*, Michael; Härtle, Birgit; Guillaume, Anna; Psiorz, Manfred (2000). "Production of Amarogentin in Root Cultures of Swertia chirata". Planta Medica 66 (5): 452–7. doi:10.1055/s-2000-8579. PMID 10909267.
- ↑ Heilpflanzen:Gentiana lutea (German)
- ↑ Behrens, Maik; Brockhoff, Anne; Batram, Claudia; Kuhn, Christina; Appendino, Giovanni; Meyerhof, Wolfgang (2009). "The Human Bitter Taste Receptor hTAS2R50 is Activated by the Two Natural Bitter Terpenoids Andrographolide and Amarogentin". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 57 (21): 9860–6. doi:10.1021/jf9014334. PMID 19817411.
- ↑ Wang, Chang-Zeng; Maier, Ulrich H.; Eisenreich, Wolfgang; Adam, Petra; Obersteiner, Ingrid; Keil, Michael; Bacher, Adelbert; Zenk, Meinhart H. (2001). "Unexpected Biosynthetic Precursors of Amarogentin − A Retrobiosynthetic13C NMR Study". European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2001 (8): 1459. doi:10.1002/1099-0690(200104)2001:8<1459::AID-EJOC1459>3.0.CO;2-0.
- ↑ Medda, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S; Basu, MK (1999). "Evaluation of the in-vivo activity and toxicity of amarogentin, an antileishmanial agent, in both liposomal and niosomal forms". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 44 (6): 791–4. doi:10.1093/jac/44.6.791. PMID 10590280.
- ↑ Ray, Sutapa; Majumder, Hemanta K.; Chakravarty, Ajit K.; Mukhopadhyay, Sibabrata; Gil, Roberto R.; Cordell, Geoffrey A. (1996). "Amarogentin, a Naturally Occurring Secoiridoid Glycoside and a Newly Recognized Inhibitor of Topoisomerase I fromLeishmania donovani". Journal of Natural Products 59 (1): 27–9. doi:10.1021/np960018g. PMID 8984149.
 |
