Chemistry:Ammonium ozonide
From HandWiki
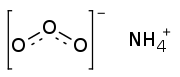
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H4NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 66.036 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep red solid |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ammonium nitrate |
Other cations
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Ammonium ozonide is an oxygen rich molecule containing an ammonium cation (NH4+) and an ozonide anion (O3−). Ammonium ozonide, like alkali ozonides, is a red solid.[1][2] Ammonium ozonide is stable at low temperatures, but it decomposes to ammonium nitrate at temperatures above -70 °C.[2]
Preparation and decomposition
Ammonium ozonide is made by bubbling gaseous ozone through liquid ammonia at -110 °C.[1][2] This method suffers from a low yield.[1]
- 12 NH
3 + 11 O
3 → 9 NH
4O
3 + 3 NO
2
Ammonium ozonide decomposes into ammonium nitrate, oxygen gas, and water. If the above reaction is done at high temperatures, these decomposition products result immediately and no ozonide is formed.[1]
- 4 NH
4O
3 → 2 NH
4NO
3 + O
2 + 4 H
2O
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Solomon, Irvine J.; Hattori, Kiyo.; Kacmarek, Andrew J.; Platz, Gerald M.; Klein, Morton J. (January 1962). "Ammonium Ozonide" (in en). Journal of the American Chemical Society 84 (1): 34–36. doi:10.1021/ja00860a008. ISSN 0002-7863. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja00860a008.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 McGee, Henry (July 1966). Chemical Reactivity of Hydrogen, Nitrogen, and Oxygen Atoms at Temperatures below 100° K (Report). pp. 1–98. A-661. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19660027917/downloads/19660027917.pdf.
 |
