Chemistry:Aurin
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
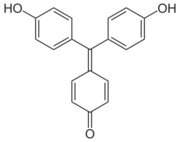
4-[Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)methylidene]cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one | |
| Other names
Aurin, corallin, p-rosolic acid, C.I. 43800
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 2055205 | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 290.318 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | see text |
| Density | 1.283 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 308 °C (586 °F; 581 K) (decomposes) |
| Insoluble | |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 482 nm[1] |
| -161.4·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1]
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H315, H319, H335[1] | |
| P261, P305+351+338[1] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aurin (C.I. 43800), sometimes named rosolic acid or corallin is an organic compound, forming yellowish or deep-red crystals with greenish metallic luster. It is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol. It is soluble in strong acids to form yellow solution, or in aqueous alkalis to form carmine red solutions.
| Aurin (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 5.0 | above pH 6.8 | |
| 5.0 | ⇌ | 6.8 |
Due to this behaviour it can be used as pH indicator with pH transition range 5.0 - 6.8. It is used as an intermediate in manufacturing of dyes.
Synthesis
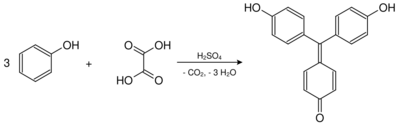
Aurin was first prepared in 1834 by the German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge, who obtained it by distilling coal tar. He named it Rosölsäure or Rosaölsäure (red oil acid).[2][3] In 1861, the German chemists Hermann Kolbe and Rudolf Schmitt presented the synthesis of aurin by heating oxalic acid and creosote (which contains phenol) in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid.[4] (Gradually, chemists realized that commercial aurin was not a pure compound, but was actually a mixture of similar compounds.[5][6])
Aurin is formed by heating of phenol and oxalic acid in concentrated sulfuric acid.
Safety
Aurin may cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion and inhalation should be avoided.
Aurin was reported to have endocrine disruptor chemical (EDC) properties.[7]:149
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Sigma-Aldrich Co., p-Rosolic acid. Retrieved on 2014-05-06.
- ↑ Runge, F. F. (1834). "Ueber einige Produkte der Steinkohlendestillation" (in German). Annalen der Physik und Chemie 31: 65–78. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=nyp.33433062753029;view=1up;seq=87. ; see p. 70.
- ↑ In 1859, the German-English chemist Hugo Müller (de) (1833–1915) found that rosolic acid could be produced simply by mixing phenol and calcium carbonate and then exposing the mixture to air for a prolonged time. Müller, Hugo (1859). "Note on rosolic acid". Quarterly Journal of the Chemical Society 11 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1039/QJ8591100001. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=njp.32101046329080;view=1up;seq=11.
- ↑ Kolbe, H.; Schmitt, R. (1861). "Rother Farbstoff aus dem Kreosot" (in German). Annalen der Chemie 119: 169–172. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uva.x002457957;view=1up;seq=181.
- ↑ See the papers of the English chemist Richard S. Dale and the German-English chemist Carl Schorlemmer and of the German chemist Heinrich Fresenius (de) (1847–1920).
- Dale, R.S.; Schorlemmer, C. (1871). "On aurin". Journal of the Chemical Society 24: 466–467. doi:10.1039/JS8712400466. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.hx1dr8;view=1up;seq=504.
- Dale, R.S.; Schorlemmer, C. (1872). "On aurin". Journal of the Chemical Society 25: 74–75. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.hx1dr9;view=1up;seq=82.
- Dale, R.S.; Schorlemmer, C. (1873). "On aurin". Journal of the Chemical Society 26: 434–444. doi:10.1039/JS8732600434. https://books.google.com/books?id=h-41AQAAMAAJ&pg=PA434.
- Dale, R.S.; Schorlemmer, C. (1879). "On aurin, part II". Journal of the Chemical Society 35: 148–159. doi:10.1039/CT8793500148. https://books.google.com/books?id=WSxEAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA148.
- Fresenius, H. (1871). "Ueber Rosolsäure" (in German). Journal für praktische Chemie. 2nd series 3: 477–480. doi:10.1002/prac.18710030149. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=njp.32101076786365;view=1up;seq=491.
- A review of findings about aurin up to 1872 appeared in: Fresenius, H. (1872). "Ueber das Corallin" (in German). Journal für praktische Chemie. 2nd series 5 (4): 184–191. doi:10.1002/prac.18720050117. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=pst.000067439980;view=1up;seq=196.
- Fresenius, H. (1872). "Corallin". Journal of the Chemical Society 25: 705–706. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.hx1dr9;view=1up;seq=749.
- ↑ Thorpe, Thomas Edward, ed., A Dictionary of Applied Chemistry, 2nd ed. (London, England: Longmans, Green, and Co., 1913), vol. 5, "Triphenylmethane colouring matters," p. 551. From p. 551: "The researches of Dale and Schorlemmer, Zulkowski, and others have shown that common aurin consists of a mixture of a number of substances, which, in a pure state, are well crystallised."
- ↑ "The Estrogen Receptor Relative Binding Affinities of 188 Natural and Xenochemicals: Structural Diversity of Ligands". Toxicological Sciences 54 (1): 138–153. 1 March 2000. doi:10.1093/toxsci/54.1.138. ISSN 1096-0929. PMID 10746941.
External links
- MSDS at Oxford University
- History of aurin in Heinrich Caro and the creation of modern chemical industry
 "Aurin". New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
"Aurin". New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
 |