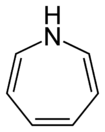
Chemistry:Azepine
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Azepine
| |||
| Other names
Azacycloheptatriene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 93.129 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Azepines are unsaturated heterocycles of seven atoms, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon at one position.[1][2]
See also
References
 |
- ↑ Smith, Jason A.; Molesworth, Peter P.; Hyland, Christopher J. T.; Ryan, John H. (2011-01-01), Gribble, Gordon; Joule, John A., eds. (in en), Chapter 7 - Seven-Membered Rings, Progress in Heterocyclic Chemistry, 22, Elsevier, pp. 491–536, doi:10.1016/S0959-6380(11)22016-6, ISBN 9780080966854, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959638011220166, retrieved 2023-01-05
- ↑ Császár, Attila G.; Demaison, Jean; Rudolph, Heinz Dieter (2015-03-05). "Equilibrium structures of three-, four-, five-, six-, and seven-membered unsaturated N-containing heterocycles". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 119 (9): 1731–1746. doi:10.1021/jp5084168. ISSN 1520-5215. PMID 25340501. Bibcode: 2015JPCA..119.1731C. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25340501/.