Chemistry:Beta-Lysine
From HandWiki
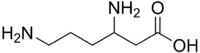
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,6-Diaminohexanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.190 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
β-Lysine (3,6-diaminohexanoic acid[1]) is an amino acid produced by platelets during coagulation and is directly antibacterial by causing lysis of many Gram positive bacteria by acting as a cationic detergent.[2]
References
- ↑ curehunter.com > beta-lysine Retrieved on April 18, 2010
- ↑ IMMUNOLOGY - CHAPTER ONE > INNATE (NON-SPECIFIC) IMMUNITY Gene Mayer, Ph.D. Immunology Section of Microbiology and Immunology On-line. University of South Carolina
 |

