Chemistry:Binapacryl
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
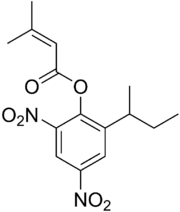
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Butan-2-yl)-4,6-dinitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate | |
| Other names
2-[(2RS)-Butan-2-yl]-4,6-dinitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate
(RS)-2-(Butan-2-yl)-4,6-dinitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate (RS)-2-sec-Butyl-4,6-dinitrophenyl 3-methylbut-2-enoate Dapacryl Morocide Morrocid Acricid Endosan Ambox Dinoseb methacrylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2779 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H18N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 322.317 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 66 to 67 °C (151 to 153 °F; 339 to 340 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H312, H360, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P273, P280, P281, P301+312, P302+352, P308+313, P312, P322, P330, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Binapacryl was used as a miticide and fungicide. Chemically, it is an ester derivative of dinoseb. Although binapacryl has low toxicity itself, it is readily metabolized to form dinoseb, which is highly toxic.[1]
International trade in binapacryl is regulated by the Rotterdam Convention; it has been withdrawn as a pesticide, since products were highly toxic to mammals, fish and aquatic invertebrates.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Datasheet from International Programme on Chemical Safety
- ↑ Pesticide Properties DataBase: Binapacryl
 |

