Chemistry:Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bis(trimethylsilyl)-λ4-sulfanediimine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
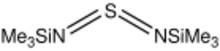
| C6H18N2SSi2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.45 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.877 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 59–61 °C (138–142 °F; 332–334 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H226, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P337+313, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide is the organosulfur compound with the formula S(NSiMe3)2 (Me = CH3). A colorless liquid, it is a diaza analogue of sulfur dioxide, i.e., a sulfur diimide. It is a reagent in the synthesis of sulfur nitrides. For example, it is a precursor to C2(N2S)2.[1]
Bis(trimethylsilyl)sulfur diimide is prepared by the reaction of thionyl chloride and sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide:[2]
- SOCl2 + 2 NaN(SiMe3)2 → S(NSiMe3)2 + 2 NaCl + O(SiMe3)2
References
- ↑ Makarov, Alexander Yu.; Irtegova, Irina G.; Vasilieva, Nadezhda V.; Bagryanskaya, Irina Yu.; Borrmann, Tobias; Gatilov, Yuri V.; Lork, Enno; Mews, Ruediger et al. (2005). "[1,2,5]Thiadiazolo[3,4-c][1,2,5]thiadiazolidyl: A Long-Lived Radical Anion and Its Stable Salts". Inorganic Chemistry 44 (20): 7194–7199. doi:10.1021/ic050583j. PMID 16180884.
- ↑ Scherer, Otto J.; Wies, Reinhard (1970). "Synthese eines siliciumorganischen cyclischen Schwefeldiimids (Synthesis of an Organosilicon Cyclic Sulfur Diimide)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 25B: 1486-7. doi:10.1515/znb-1970-1240.

