Chemistry:Butenoic acid
From HandWiki
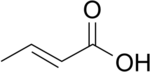
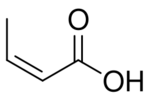
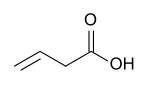
Butenoic acid is any of three monocarboxylic acids with an unbranched 4-carbon chain with 3 single bonds and one double bond; that is, with the structural formula HO(O=)C–CH=CH–CH2–H (2-butenoic) or HO(O=)C–CH2–CH=CH–H (3-butenoic). All have the chemical formula C3H5COOH or C4H6O2.
These compounds are technically mono-unsaturated fatty acids, although some authors may exclude them for being too short. The three isomers are:
- crotonic acid (trans-2-butenoic or (2E)-but-2-enoic acid)
- isocrotonic acid (cis-2-butenoic or (2Z)-but-2-enoic acid)
- 3-butenoic acid (but-3-enoic acid).[1][2]
See also
- Methacrylic acid, also C3H5COOH but branched like isobutene; a.k.a. isobutenoic acid
- Butyric acid, C3H7COOH; a.k.a. butanoic acid
References
- ↑ M. A. Casado-Rodriguez, M. Sanchez-Molina, A. Lucena-Serrano, C. Lucena-Serrano, B. Rodriguez-Gonalez, Manuel Algarra, Amelia Diaz, M. Valpuesta, J. M. Lopez-Romero, J. PerezJuste, and R. Contreras-Caceres (2016): "Synthesis of vinyl-terminated Au nanoprisms and nanooctahedra mediated by 3-butenoic acid: Direct Au@pNIPAM fabrication with improved SERS capabilities". Nanoscale, volume 2016, issue 8, pages 4557-4564. doi:10.1039/C5NR08054A
- ↑ David B. Bigley and Michael J. Clarke (1982): "Studies in decarboxylation. Part 14. The gas-phase decarboxylation of but-3-enoic acid and the intermediacy of isocrotonic (cis-but-2-enoic) acid in its isomerisation to crotonic (trans-but-2-enoic) acid". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2, volume 2, issue 1, pages 1-6. doi:10.1039/P29820000001
| |
This article includes a list of related items that share the same name (or similar names). If an internal link incorrectly led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
 |