Chemistry:Capillin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
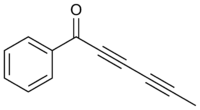
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Phenylhexa-2,4-diyn-1-one | |
| Other names
Capillin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8O | |
| Molar mass | 168.195 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 82–83 °C |
| 0.0177 mg/mL | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Capillin is a naturally occurring organic compound with the chemical formula C12H8O. The structure contains acetophenone and a polyyne (pentadiynyl) portion, conjugated together as an ynone.
Chemical taxonomy
Capillin is found in the essential oil of a number of Artemisia species, including Artemisia monosperma and Artemisia dracunculus (tarragon).[1] The substance was initially isolated from Artemisia capillaris in 1956.[2]
Applications
Capillin is a biologically active substance. It has strong antifungal activity, and it is possibly antitumoral. Capillin exhibits cytotoxic activity and could cause apoptosis of certain human tumor cells.[3]
References
- ↑ Wishart, David S.; Djombou Feunang, Yannick; Marcu, Ana; Guo, An Chi; Liang, Kevin; Vázquez Fresno, Rosa; Sajed, Tanvir; Johnson, Daniel et al.. "Showing metabocard for Capillin (HMDB32867)". http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB32867.
- ↑ Nash, B. W.; Thomas, D. A.; Warburton, W. K.; Williams, Thelma D. (1965). "535. The preparation of capillin and some related compounds, and of some substituted pent-4-en-2-yn-1-ones". J. Chem. Soc.: 2983–2988. doi:10.1039/JR9650002983.
- ↑ "Effects of the polyacetylene capillin on human tumour cell lines". Anticancer Research 24 (4): 2281–6. 2004. PMID 15330173.
 |
