Chemistry:Cetadiol
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
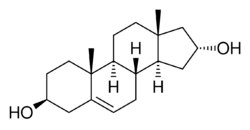 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Androst-5-ene-3β,16α-diol; 3β,16α-Dihydroxy-5-androstene |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 290.447 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cetadiol, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,16α-diol, is a drug described as a "steroid tranquilizer" which was briefly investigated as a treatment for alcoholism in the 1950s.[1][2][3][4][5] It is an androstane steroid and analogue of 5-androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol) and 16α-hydroxy-DHEA (androst-5-ene-3β,16α-diol-17-one), but showed no androgenic or myotrophic activity in animal bioassays.[4] The drug was reported in 1956 and studied until 1958.[1]
Chemistry
See also
- Androstadienol (androsta-5,16-dien-3β-ol)
- Androstenol (5α-androst-16-en-3α-ol)
- 4-Androstadienol (PH94B; Aloradine)
- Cyclopregnol
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. 14 November 2014. pp. 86–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA86.
- ↑ Organic-chemical drugs and their synonyms: (an international survey). Wiley-VCH. 2001. p. 1841. ISBN 978-3-527-30247-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=zmpqAAAAMAAJ.
- ↑ "New steroid hormone tranquilizing agent (cetadiol)". The American Journal of Psychiatry 113 (10): 930. April 1957. doi:10.1176/ajp.113.10.930. PMID 13402989.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Cetadiol (5-androstene-3 16-diol) in the treatment of hospitalized alcoholics". The American Journal of Psychiatry 112 (10): 845. April 1956. doi:10.1176/ajp.112.10.845. PMID 13302491.
- ↑ "The effect of cetadiol on delirium tremens, alcoholic hallucinosis, and alcohol withdrawal". The American Journal of Psychiatry 114 (10): 935–936. April 1958. doi:10.1176/ajp.114.10.935. PMID 13508929.
 |

