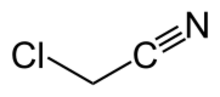
Chemistry:Chloroacetonitrile
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Chloroacetonitrile | |
| Other names
α-Chloroacetonitrile
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2668 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2ClN | |
| Molar mass | 75.50 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.193 g·cm−3 |
| Boiling point | 123–124 °C (253–255 °F; 396–397 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H311, H331, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chloroacetonitrile is the organic compound with the formula ClCH2CN. A colorless liquid, it is derived from acetonitrile (CH3CN) by replacement of one H with Cl. In practice, it is produced by dehydration of chloroacetamide.[1] The compound is an alkylating agent,[2] and as such is handled cautiously.
Chloroacetonitrile is also generated in situ by the reaction of acetonitrile with sulfur monochloride. A second chlorination gives dichloroacetonitrile, which undergoes cycloaddition with sulfur monochloride to give 4,5-dichloro-1,2,3-dithiazolium chloride:[3]
- Cl2CHCN + S2Cl2 → [S2NC2Cl2]Cl + HCl
References
- ↑ Reisner, D. B.; Horning, E. C. (1950). "Chloroacetonitrile". Organic Syntheses 30: 22. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.030.0022.
- ↑ Lebeuf, Raphaël; Berlande, Muriel; Robert, Frédéric; Landais, Yannick (2009). "Preparation of (3,5-Dimethoxy-1-Phenyl-Cyclohexa-2,5-Dienyl)-Acetonitrile Through Birch Reductive Alkylation (BRA)". Organic Syntheses 86: 1. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.086.0001.
- ↑ Rees, Charles W. (1992). "Polysulfur-Nitrogen Heterocyclic Chemistry". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 29 (3): 639–651. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570290306.
 |

