Chemistry:Copaene
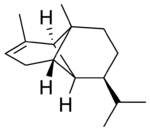 (−)-α-Copaene
| |
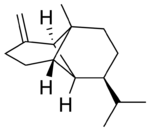 (−)-β-Copaene
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
α: (1R,2S,6S,7S,8S)-8-isopropyl-1,3-dimethyltricyclo[4.4.0.02,7]dec-3-ene
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.939 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 124 °C (255 °F; 397 K) (15 mmHg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Copaene, or more precisely, α-copaene, is the common (or trivial) chemical name of an oily liquid hydrocarbon that is found in a number of essential oil-producing plants. The name is derived from that of the resin-producing tropical copaiba tree, Copaifera langsdorffii, from which the compound was first isolated in 1914. Its structure, including the chirality, was determined in 1963.[1] The double-bond isomer with an exocyclic-methylene group, β-copaene, was first reported in 1967.[2]
Chemically, the copaenes are tricyclic sesquiterpenes. The molecules are chiral, and the α-copaene enantiomer most commonly found in higher plants exhibits a negative optical rotation of about −6°. The rare (+)-α-copaene is also found in small amounts in some plants. (+)-α-copaene is of economic significance because it is strongly attracting to an agricultural pest, the Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata.[3]
References
- ↑ V.H. Kapadia et al. (1963). "Structure of mustakone and copaene". Tetrahedron Letters 4 (28): 1933. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)90945-1.
- ↑ L. Westfelt; Westfelt, Lars; Sky, K.; Nilsson, Åke; Theorell, H.; Blinc, R.; Paušak, S.; Ehrenberg, L. et al. (1967). "Beta-Copaene and beta-Ylangene, Minor Sesquiterpenes of the Wood of Pinus silvestris L. And of Swedish Sulphate Turpentine". Acta Chemica Scandinavica 21: 152. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-0152.
- ↑ R. Nishida et al. (2000). Journal of Chemical Ecology 26: 87. doi:10.1023/A:1005489411397.
 |
