Chemistry:Decahydroisoquinoline
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-Decahydroisoquinoline
| |
| Other names
Perhydroisoquinoline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H17N | |
| Molar mass | 139.242 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
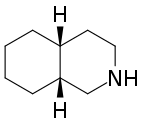
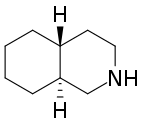
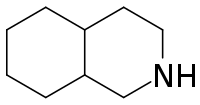
Decahydroisoquinoline is a nitrogen-containing heterocycle with the chemical formula C
9H
17N.[1] It is the saturated form of isoquinoline.
Decahydroisoquinoline can be formed by the hydrogenation of isoquinoline or tetrahydroisoquinoline.[2]
Isomers
There are four stereoisomers of decahydroisoquinoline which differ by the configuration of the two carbon atoms at the ring fusion:
(4aR,8aR)‐cis-decahydroisoquinoline
(4aS,8aS)‐cis-decahydroisoquinoline
(4aR,8aS)‐trans-decahydroisoquinoline
(4aS,8aR)‐trans-decahydroisoquinoline
Occurrence
The decahydroisoquinoline occurs naturally in some alkaloids, including gephyrotoxins and pumiliotoxin C which are found in amphibian skins.[3]
A variety of pharmaceutical drugs include a decahydroisoquinoline ring system within their structure, including ciprefadol,[4] dasolampanel,[5] nelfinavir,[6] saquinavir,[7] and tezampanel.[8]
References
- ↑ Template:Pubchem
- ↑ Okazaki, Hiroshi; Soeda, Mahito; Ikefuji, Yoshio; Tamura, Ryuji (1988). "Selective hydrogenation of neat isoquinoline". Applied Catalysis 43: 71–84. doi:10.1016/S0166-9834(00)80901-X.
- ↑ Daly, John W.; Martin Garraffo, H.; Spande, Thomas F. (1999). Alkaloids from Amphibian Skins. Alkaloids: Chemical and Biological Perspectives. 13. pp. 1–161. doi:10.1016/S0735-8210(99)80024-7. ISBN 9780080434032.
- ↑ "Ciprefadol". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/333483#section=Names-and-Identifiers.
- ↑ "Dasolampanel". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/51049972#section=Names-and-Identifiers.
- ↑ "Nelfinavir". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/64143#section=Names-and-Identifiers.
- ↑ "Saquinavir". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/441243#section=Names-and-Identifiers.
- ↑ "Tezampanel". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/127894#section=Names-and-Identifiers.
 |