Chemistry:Dimedone
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5,5-Dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione | |||
| Other names
Cyclomethone,
5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione, Dimethyldihydroresorcinol, Methone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H12O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 140.182 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White solid | ||
| Melting point | 147 to 150 °C (297 to 302 °F; 420 to 423 K) (decomposes) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Dimedone is an organic compound with the formula (CH
3)
2C(CH
2)
2(CO)
2(CH
2). Classified as a cyclic diketone, it is a derivative of 1,3-cyclohexanedione. It is a white solid that is soluble in water, as well as ethanol and methanol. It once was used as a reagent to test for the aldehyde functional group.
Synthesis
Dimedone is prepared from mesityl oxide and diethyl malonate via a Michael addition reaction.[1][2]
Chemical properties
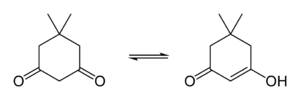
Tautomerism
Dimedone is in equilibrium with its tautomer in solution — in a 2:1 keto to enol ratio in chloroform.[3]
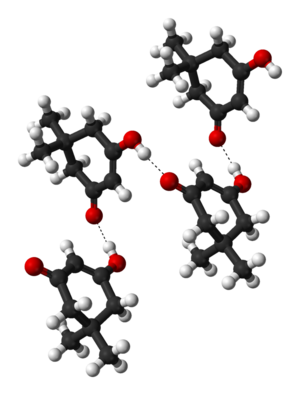
Crystalline dimedone contains chains of molecules, in the enol form, linked by hydrogen bonds:[4]
Reaction with aldehydes
Dimedone reacts with aldehydes to give crystalline derivatives, whose melting points can be used to distinguish between aldehydes.[5]
References
- ↑ R. L. Shriner and H. R. Todd (1935). "5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione". Organic Syntheses 15: 16. doi:10.1002/0471264180.os015.06. ISBN 0471264229. http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv2p0200.
- ↑ "Dimedone synthesis" (in en). https://www.chemtube3d.com/conjugate-addition-dimedone-synthesis/.
- ↑ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 530. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ↑ M. Bolte and M. Scholtyssik (October 1997). "Dimedone at 133K". Acta Crystallogr. C 53 (10): IUC9700013. doi:10.1107/S0108270197099423.
- ↑ Horning, E. C.; Horning, M. G. (1946). "Methone Derivatives of Aldehydes" (in en). The Journal of Organic Chemistry 11 (1): 95–99. doi:10.1021/jo01171a014. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 21013441. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo01171a014.
 |