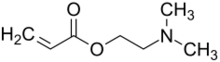
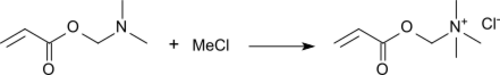Chemistry:Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl prop-2-enoate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3302 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H13NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 143.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellowish liquid with a pungent, amine-like odor[1] |
| soluble in water (240 g/L[1]) upon hydrolysis, miscible with organic solvents[2] | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |     
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H302, H311, H314, H317, H330, H400, H412 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P320, P321 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate (2-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate) or DMAEA is an unsaturated carboxylic acid ester having a tertiary amino group. It is a colorless to yellowish, water-miscible liquid with a pungent, amine-like odor. DMAEA is an important acrylic monomer that gives basic properties to copolymers.
Preparation
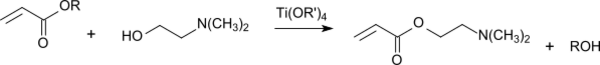
2-Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate is prepared via transesterification of acrylic acid esters such as methyl acrylate (R = -CH3)[3] or ethyl acrylate (R = -CH2-CH3)[4] with 2-dimethylaminoethanol under acid catalysis with tin compounds (for example stannoxanes[5]) or titanium compounds (for example tetraisopropyl orthotitanate[6]). More than 95% yield can be achieved.[7]
During the reaction, inhibitors must be present (such as phenothiazine), because of the high tendency of starting material and product to polymerize. When ethyl acrylate is used as a reactant, ethanol is formed; this forms with the ethyl acrylate an azeotrope of the composition ethanol/ethyl acrylate 72.7:26.3%, which boils at 77.5 °C under atmospheric pressure.[8] To achieve a high reaction yield, the ethanol is distilled off from the reaction mixture. The product is purified by vacuum distillation and stabilized with about 1,000 ppm 4-methoxyphenol (MEHQ).
Properties
Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate is a clear, colorless to slightly yellowish liquid with a pungent amine-like odor. It is miscible with water, reacts bases and hydrolyzes rapidly to acrylic acid and dimethylaminoethanol. It can form ignitable mixtures with air. DMAEA tends to spontaneously polymerize at elevated temperatures, upon irradiation, and in the presence of free-radical initiators. It must therefore be adequately stabilized, stored in a dry and cool place (<25 °C). DMAEA is very toxic because of its high inhalation toxicity.[1]
Use
Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate is an acrylic acid ester carrying a functional group with basic properties. It therefore reacts as an α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound in an addition reaction with nucleophiles in a Michael addition.
As a reactive monomer, 2-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate forms homopolymers and copolymers with acrylic acid and acrylic acid salts, amides and esters, as well as methacrylates, acrylonitrile, maleic acid esters, vinyl acetate, chloroethene (vinyl chloride), 1,1-dichloroethene, styrene, 1,3-butadiene, unsaturated polyesters and drying oils. In copolymers, DMAEA improves their nucleophilicity, basicity, water solubility and adhesion to polar negatively charged substrates, as well as dyeability of acrylic fibers with anionic dyes. Such copolymers are used as resins and paints, coatings and adhesives, as well as hair spray.
The most significant use for DMAEA is the quaternization with alkylating agents (for example chloromethane, dimethyl sulfate or benzyl chloride) to the quaternary ammonium salt.[9]
The most important compound is the reaction product with methyl chloride, trimethylammonium ethyl acrylate chloride.[10] It has the most pronounced cationic properties of all acrylates and is traded as an 80% aqueous solution. Copolymerization of trimethylammoniumethyl acrylate chloride with acrylamide leads to high molecular weight cationic polyacrylamides, which are widely used as coagulants and flocculants[11] in waste water purification and as retention and dewatering agents in papermaking.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Record of 2-(Dimethylamino)ethylacrylat in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 1 February 2016.
- ↑ Sicherheitsdatenblatt DIMETHYLAMINOETHYLACRYLAT, BASF AG, überarbeitet 13 December 2010.
- ↑ P. Jiang et al., A new catalytic transesterification for the synthesis of N,N-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate with organotin catalyst, Catalysis Letters, vol. 110, 101, August 2006, doi:10.1007/s10562-006-0091-1.
- ↑ "Process for the continuous manufacturing of dialkylaminoalkyl (meth)acrylates having a critical order of steps" US patent 6437173, issued 2002-08-20, assigned to Elf Atochem S.A.
- ↑ "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Aminoalkyl(meth)acrylaten" EP patent 1299345, issued 2003-04-09, assigned to Stockhausen GmbH
- ↑ Deutsche Offenlegungsschrift DE 10127939 A1, Verfahren zur Herstellung von (Meth)acrylsäureestern, invent1: M. Geissendörfer et al., assign1: BASF AG, offengelegt 29 May 2002.
- ↑ "Process for the manufacture of dialkylaminoalkyl (meth)acrylates" US patent 4851568, issued 1985-07-25, assigned to Elf Atochem S.A.
- ↑ Technical Data Sheet, Ethyl Acrylate, BASF AG, June 2002.
- ↑ "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Trialkylammoniumalkyl(meth)acryl-Verbindungen" EP patent 0604844, issued 1994-07-06, assigned to Röhm GmbH
- ↑ Arkema S.A.: 2-dimethylaminoethyl acrylate, retrieved 6 December 2016.
- ↑ SNF Floerger, Water Treatment
 |