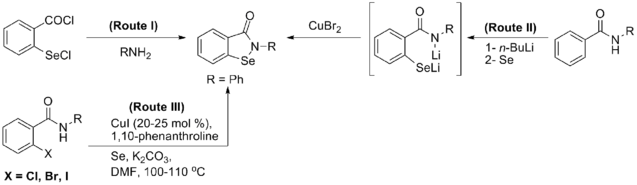
Chemistry:Ebselen
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H9NOSe | |
| Molar mass | 274.17666 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ebselen (also called PZ 51, DR3305, and SPI-1005), is a synthetic organoselenium drug molecule with anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and cytoprotective activity. It acts as a mimic of glutathione peroxidase and can also react with peroxynitrite.[1] It is being investigated as a possible treatment for reperfusion injury and stroke,[2][3] Ménière's disease,[4][5] hearing loss and tinnitus,[6][7] and bipolar disorder.[8][9]
Additionally, ebselen may be effective against Clostridioides difficile infections[10] and has been shown to have antifungal activity against Aspergillus fumigatus.[11]
Ebselen is a potent scavenger of hydrogen peroxide as well as hydroperoxides including membrane bound phospholipid and cholesterylester hydroperoxides. Several ebselen analogs have been shown to scavenge hydrogen peroxide in the presence of thiols.[12]
Possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity
Preliminary studies demonstrate that Ebselen exhibits promising inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 in cell-based assays.[13][14][15] The effect was attributed to irreversible inhibition of the main protease via a covalent bond formation with the thiol group of the active center's cysteine (Cys-145).[13]
Synthesis
Generally, synthesis of the characteristic scaffold of ebselen, the benzoisoselenazolone ring system, can be achieved either through reaction of primary amines (RNH2) with 2-(chloroseleno)benzoyl chloride (Route I),[16] by ortho-lithiation of benzanilides followed by oxidative cyclization (Route II) mediated by cupric bromide (CuBr2),[17] or through the efficient Cu-catalyzed selenation / heterocyclization of o-halobenzamides, a methodology developed by Kumar et al.[18] (Route III).
History
The first patent for 2-Phenyl-1,2-benzoselenazol-3(2H)-one was filed in 1980 and granted in 1982.[19]
References
- ↑ "Molecular actions of ebselen--an antiinflammatory antioxidant". General Pharmacology 26 (6): 1153–69. October 1995. doi:10.1016/0306-3623(95)00003-J. PMID 7590103.
- ↑ "Ebselen: prospective therapy for cerebral ischaemia". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 9 (3): 607–19. March 2000. doi:10.1517/13543784.9.3.607. PMID 11060699.
- ↑ "Ebselen in acute ischemic stroke: a placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Ebselen Study Group". Stroke 29 (1): 12–7. January 1998. doi:10.1161/01.STR.29.1.12. PMID 9445321.
- ↑ "SPI-1005 for the Treatment of Meniere's Disease". Sound Pharmaceuticals. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04677972.
- ↑ "Sound Pharma initiates enrollment in pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial of SPI-1005 for the treatment of hearing loss and tinnitus in Meniere's disease". Sound Pharmaceuticals. 2022-07-28. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/sound-pharma-initiates-enrollment-in-pivotal-phase-3-clinical-trial-of-spi-1005-for-the-treatment-of-hearing-loss-and-tinnitus-in-menieres-disease-301595208.html.
- ↑ "Ebselen treatment reduces noise induced hearing loss via the mimicry and induction of glutathione peroxidase". Hearing Research 226 (1–2): 44–51. April 2007. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2006.08.006. PMID 17030476.
- ↑ Kil, Jonathan; Harruff, E. Emily; Longenecker, Ryan J. (2022). "Development of ebselen for the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus". Hearing Research (Elsevier BV) 413: 108209. doi:10.1016/j.heares.2021.108209. ISSN 0378-5955. PMID 33678494.
- ↑ "A safe lithium mimetic for bipolar disorder". Nature Communications 4: 1332. 2013. doi:10.1038/ncomms2320. PMID 23299882. Bibcode: 2013NatCo...4.1332S.
- ↑ "New drug for bipolar disorder may offer fewer side effects". University of Oxford Latest News. 2013-01-08. http://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2013-01-08-new-drug-bipolar-disorder-may-offer-fewer-side-effects.
- ↑ "Drug disarms deadly C. difficile bacteria without destroying healthy gut flora". Medical Express. http://medicalxpress.com/news/2015-09-drug-deadly-difficile-bacteria-healthy.html.
- ↑ "Structure, Mechanism, and Inhibition of Aspergillus fumigatus Thioredoxin Reductase". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 63 (3): e02281-18. March 2019. doi:10.1128/AAC.02281-18. PMID 30642940.
- ↑ "Synthesis and antioxidant activity of peptide-based ebselen analogues". Chemistry: A European Journal 17 (17): 4849–57. April 2011. doi:10.1002/chem.201003417. PMID 21400619.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors". Nature 582 (7811): 289–293. June 2020. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y. PMID 32272481. Bibcode: 2020Natur.582..289J.
- ↑ "Identification of ebselen and its analogues as potent covalent inhibitors of papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2". Scientific Reports 11 (1): 3640. February 2021. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-83229-6. PMID 33574416. Bibcode: 2021NatSR..11.3640W.
- ↑ "Recent advances in developing small-molecule inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 12 (4): 1591–1623. July 2021. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.06.016. PMID 34249607.
- ↑ "Photochemical Reaction of 2-Aryl-1, 2-benzisoselenazol-3 (2 H)-ones.". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 59 (7): 2179–83. July 1986. doi:10.1246/bcsj.59.2179.
- ↑ "Expedient synthesis of ebselen and related compounds". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 54 (12): 2964–2966. 1989-06-01. doi:10.1021/jo00273a035. ISSN 0022-3263.
- ↑ "Cu-catalyzed efficient synthetic methodology for ebselen and related Se-N heterocycles". Organic Letters 12 (23): 5394–7. December 2010. doi:10.1021/ol102027j. PMID 21053969.
- ↑ , Eugen Dr; Marcel Prof Dipl-Chem Jupille Renson & Johannes Dr 5000 Köln Winkelmann"2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2h)-on enthaltende pharmazeutische praeparate und ihre verwendung" patent DE3027073A1, issued 1982-02-18
 |