Chemistry:Eckol
From HandWiki
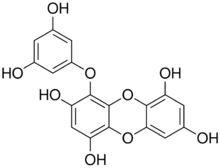
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenoxy)oxanthrene-1,3,6,8-tetrol | |
| Other names
1-(3,5-Dihydroxyphenoxy)-2,4,7,9-tetrahydroxydibenzo-1,4-dioxin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H12O9 | |
| Molar mass | 372.285 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Eckol is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae in the family Lessoniaceae such as species in the genus Ecklonia[1] such as E. cava[2] or E. kurome[3] or in the genus Eisenia such as Eisenia bicyclis.[4]
The molecule possesses a dibenzo-p-dioxin skeleton and a phloroglucinol component. The molecule can also be viewed as a phloroglucinol trimer.[5]
It exhibits an antiplasmin inhibitory effect[3] and a radioprotective effect in a mouse model.[1][6] It also exhibits an in vitro cytoprotective effect against oxidative stress in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts.[2] It also shows antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activities.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Moon, Changjong; Kim, Sung-Ho; Kim, Jong-Choon; Hyun, Jin Won; Lee, Nam Ho; Park, Jae Woo; Shin, Taekyun (2008). "Protective effect of phlorotannin components phloroglucinol and eckol on radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice". Phytotherapy Research 22 (2): 238–42. doi:10.1002/ptr.2298. PMID 17886227.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Kang, Kyoung Ah; Lee, Kyoung Hwa; Chae, Sungwook; Zhang, Rui; Jung, Myung Sun; Lee, Youngki; Kim, So Young; Kim, Hee Sun et al. (2005). "Eckol isolated from Ecklonia cava attenuates oxidative stress induced cell damage in lung fibroblast cells". FEBS Letters 579 (28): 6295–304. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.10.008. PMID 16253238.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fukuyama, Y; Kodama, M; Miura, I; Kinzyo, Z; Kido, M; Mori, H; Nakayama, Y; Takahashi, M (1989). "Structure of an anti-plasmin inhibitor, eckol, isolated from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome Okamura and inhibitory activities of its derivatives on plasma plasmin inhibitors". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 37 (2): 349–53. doi:10.1248/cpb.37.349. PMID 2525966.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kim, Tae Hoon; Ku, Sae-Kwang; Bae, Jong-Sup (2012). "Antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activities of eckol and dieckol". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 113 (9): 2877–83. doi:10.1002/jcb.24163. PMID 22511271.
- ↑ Shibata, Toshiyuki; Fujimoto, Ken; Nagayama, Kohki; Yamaguchi, Kuniko; Nakamura, Takashi (2002). "Inhibitory activity of brown algal phlorotannins against hyaluronidase". International Journal of Food Science and Technology 37 (6): 703. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2621.2002.00603.x.
- ↑ Nakayama, Yasuo; Takahashi, Masayuki; Fukuyama, Yoshiyasu; Kinzyo, Zyunei (1989). "Anti-plasmin inhibitor. Part IV. An anti-plasmin inhibitor, eckol, isolated from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome OKAMURA". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 53 (11): 3025. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.53.3025.
 |

