Chemistry:Emricasan
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
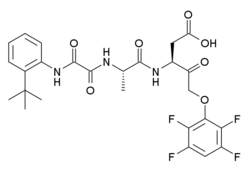
| Formula | C26H27F4N3O7 |
| Molar mass | 569.501 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Emricasan (IDN-6556, PF-03491390) is a potential drug invented in 1998 by Idun Pharmaceuticals.[1][2] The drug was acquired by Pfizer in 2005[3] and then sold to Conatus Pharmaceuticals in 2010.[1] Conatus in turn licensed emricasan to Novartis in 2017 for exclusive development and commercialization.[4]
The substance acts as a pan-caspase inhibitor and has antiapoptotic and antiinflammatory effects.[4] It was developed for the treatment of liver disease[5] and has been granted fast track designation by the FDA for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis[6][7][8] The substance is the first pan-caspase inhibitor to advance to broad clinical testing, and its novel mechanism of action has led to research using it for other potential applications.[9][10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McCallister, Erin (Aug 9, 2010). "IDUN IT AGAIN: Conatus Reacquires Idun Assets From Pfizer, Hopes Data Will Attract Investors". BioCentury. https://www.biocentury.com/biocentury/strategy/2010-08-09/conatus-reacquires-idun-assets-pfizer-hopes-data-will-attract.
- ↑ "First-in-class pan caspase inhibitor developed for the treatment of liver disease". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48 (22): 6779–82. November 2005. doi:10.1021/jm050307e. PMID 16250635.
- ↑ "Pfizer to acquire Idun Pharmaceuticals in cash transaction". Scrip. May 2005. https://scrip.pharmaintelligence.informa.com/deals/200510036.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Taylor, Phil (May 4, 2017). "Novartis adds to NASH pipeline, activating license for Conatus' emricasan". FierceBiotech. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/novartis-doubles-down-nash-activating-license-for-conatus-emricasan.
- ↑ "Characterization of IDN-6556 (3-[2-(2-tert-butyl-phenylaminooxalyl)-amino]-propionylamino]-4-oxo-5-(2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-phenoxy)-pentanoic acid): a liver-targeted caspase inhibitor". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 309 (2): 634–40. May 2004. doi:10.1124/jpet.103.062034. PMID 14742742.
- ↑ Marriott, Niamh (10 May 2017). "Lonza NEWS Novartis enter agreement with Conatus for NASH treatment". European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/51248/novartis-nash-treatment/.
- ↑ "Current opinion on 3-[2-[(2-tert-butyl-phenylaminooxalyl)-amino]-propionylamino]- 4-oxo-5-(2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-phenoxy)-pentanoic acid, an investigational drug targeting caspases and caspase-like proteases: the clinical trials in sight and recent anti-inflammatory advances". Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery 7 (3): 229–58. September 2013. doi:10.2174/1872213X113079990017. PMID 23859695.
- ↑ "Current and upcoming pharmacotherapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease". Gut 66 (1): 180–190. January 2017. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312431. PMID 27646933. https://zenodo.org/record/1236164.
- ↑ "The caspase-8 inhibitor emricasan combines with the SMAC mimetic birinapant to induce necroptosis and treat acute myeloid leukemia". Science Translational Medicine 8 (339): 339ra69. May 2016. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad3099. PMID 27194727.
- ↑ "Identification of small-molecule inhibitors of Zika virus infection and induced neural cell death via a drug repurposing screen". Nature Medicine 22 (10): 1101–1107. October 2016. doi:10.1038/nm.4184. PMID 27571349.
 |
