Chemistry:Eschenmoser's salt
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dimethylmethaniminium iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 3H 8NI | |
| Molar mass | 185.01 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless hygroscopic crystals |
| Melting point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| decomposes | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
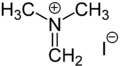
In organic chemistry, Eschenmoser's salt (named for Albert Eschenmoser) is the ionic, organic compound [(CH
3)
2NCH
2]I. It is the iodide salt of the dimethylaminomethylene cation [(CH
3)
2NCH
2]+
.
The dimethylaminomethylene cation is a strong dimethylaminomethylating agent, used to prepare derivatives of the type RCH
2N(CH
3)
2.[1][2] Enolates, silyl enol ethers, and even more acidic ketones undergo efficient dimethylaminomethylation. Once prepared, such tertiary amines can be further methylated and then subjected to base-induced elimination to afford methylidenated ketones. The salt was first prepared by the group of Albert Eschenmoser[3] after whom the reagent is named.
Structure and bonding
Dimethylaminomethylene cation is described as a resonance hybrid of the carbocation and an iminium cation:
- [math]\ce{ (CH3)2N-CH2+ <=> (CH3)2N+=CH2 }[/math]
The C
3N atoms are coplanar. The cation is isoelectronic with isobutene.
Preparation
Pyrolysis of iodomethyltrimethylammonium iodide affords the desired salt:[3]
- [math]\ce{ [(CH3)3N-CH2I]I -> [(CH3)2NCH2]I + CH3I }[/math]
An alternative route starts with bis(dimethylamino)methane:
- [math]\ce{ [(CH3)2N]2CH2 + (CH3)3SiI -> [(CH3)2NCH2]I + (CH3)3SiN(CH3)2 }[/math]
Related salts
Other salts of the dimethylaminomethylene cation:
- Dimethyl(methylidene)ammonium trifluoroacetate.[4][1]
- Dimethyl(methylidene)ammonium chloride (Böhme's salt[1], after Horst Böhme)
See also
- Vilsmeier reagent, [(CH
3)
2NCHCl]Cl.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 E. F. Kleinman in "Dimethylmethyleneammonium Iodide and Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd346
- ↑ Horst Böhme; Eberhard Mundlos; Otto-Erich Herboth (1957). "Über Darstellung und Eigenschaften α-Halogenierter Amine". Chemische Berichte 90 (9): 2003–2008. doi:10.1002/cber.19570900942.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 Jakob Schreiber; Hans Maag; Naoto Hashimoto; Albert Eschenmoser (1971). "Dimethyl(methylene)ammonium Iodide". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 10 (5): 330–331. doi:10.1002/anie.197103301.
- ↑ Gaudry, Michel; Jasor, Yves; Khac, Trung Bui (1979). "Regioselective Mannich Condensation with Dimethyl(Methylene)Ammonium Trifluoroacetate: 1-(Dimethylamino)-4-Methyl-3-Pentanone". Organic Syntheses 59: 153. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.059.0153.
 |

