Chemistry:Ethylene diurea
From HandWiki
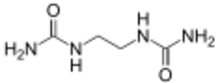
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N′′-(Ethane-1,2-diyl)diurea | |
| Other names
Ethanediurea; 1,1′-Ethylenebisurea
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.150 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 192 °C (378 °F; 465 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethylene diurea (EDU) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2NHCONH2)2. It is a white solid.
The compound has attracted interest as a potential antiozonant for crop protection. With respect to preventing the harmful effects on crops by ozone, EDU appears to either prevent the harmful effects of ozone or it stimulated plant growth.[2] Trees treated with EDU were significantly healthier in both leaf longevity and water use efficiency.[3]
The effectiveness of EDU depends upon several environmental factors.[4]
References
- ↑ Bachmann, W. E.; Horton, W. J.; Jenner, E. L.; MacNaughton, N. W.; Maxwell, C. E. (1950). "The Nitration of Derivatives of Ethylenediamine1". Journal of the American Chemical Society 72 (7): 3132–3134. doi:10.1021/ja01163a090. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ Archambualt, Daniel; Li, Xiaomei (January 2002). Evaluation of the Anti-oxidant Ethylene Diurea (EDU) as a protectant against Ozone effects on Crops. Alberta Environment. http://www.environment.gov.ab.ca/info/library/6705.pdf. Retrieved 2012-10-12.
- ↑ "Whole-tree water use efficiency is decreased by ambient ozone and not affected by O3-induced stomatal sluggishness". PLOS ONE 7 (6): e39270. 2012. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039270. PMID 22723982.
- ↑ Ribas, A.; Peñuelas, J. (2000). "Effects of Ethylene diurea as a protective antiozonant on beans (Phaseolus vulgaris cv Lit) exposed to different tropospheric ozone doses in Catalonia (NE Spain)". Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 117 (1/4): 263–271. doi:10.1023/A:1005138120490. ISSN 0049-6979.
 |

