Chemistry:Fosmidomycin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
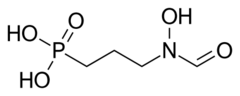
| Formula | C4H10NO5P |
| Molar mass | 183.100 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fosmidomycin is an antibiotic that was originally isolated from culture broths of bacteria of the genus Streptomyces.[1] It specifically inhibits DXP reductoisomerase, a key enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. It is a structural analogue of 2-C-methyl-D-erythrose 4-phosphate. It inhibits the E. coli enzyme with a KI value of 38 nM (4), MTB at 80 nM, and the Francisella enzyme at 99 nM.[2] Several mutations in the E. coli DXP reductoisomerase were found to confer resistance to fosmidomycin.[3][4]
Use in malaria
The discovery of the non-mevalonate pathway in malaria parasites has indicated the use of fosmidomycin and other such inhibitors as antimalarial drugs.[5] Indeed, fosmidomycin has been tested in combination treatment with clindamycin for treatment of malaria with favorable results.[6][7][8] It has been shown that an increase in copy number of the target enzyme (DXP reductoisomerase) correlates with in vitro fosmidomycin resistance in the lethal malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum.[9]
References
- ↑ "Studies on new phosphonic acid antibiotics. II. Taxonomic studies on producing organisms of the phosphonic acid and related compounds". The Journal of Antibiotics 33 (1): 19–23. January 1980. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.33.18. PMID 7372546.
- ↑ "Kinetic characterization and phosphoregulation of the Francisella tularensis 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (MEP synthase)". PLOS ONE 4 (12): e8288. December 2009. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008288. PMID 20011597. Bibcode: 2009PLoSO...4.8288J.
- ↑ "Resistance to the antimicrobial agent fosmidomycin and an FR900098 prodrug through mutations in the deoxyxylulose phosphate reductoisomerase gene (dxr)". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 59 (9): 5511–9. September 2015. doi:10.1128/AAC.00602-15. PMID 26124156.
- ↑ "Genomic Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Reductoisomerase (DXR) Mutations Conferring Resistance to the Antimalarial Drug Fosmidomycin in E. coli". ACS Synthetic Biology 7 (12): 2824–2832. November 2018. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.8b00219. PMID 30462485.
- ↑ "Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs". Science 285 (5433): 1573–6. September 1999. doi:10.1126/science.285.5433.1573. PMID 10477522.
- ↑ "Fosmidomycin-clindamycin for Plasmodium falciparum Infections in African children". The Journal of Infectious Diseases 189 (5): 901–8. March 2004. doi:10.1086/381785. PMID 14976608.
- ↑ "Fosmidomycin plus clindamycin for treatment of pediatric patients aged 1 to 14 years with Plasmodium falciparum malaria". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 50 (8): 2713–8. August 2006. doi:10.1128/AAC.00392-06. PMID 16870763.
- ↑ "Assessment of the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of two combination regimens of fosmidomycin-clindamycin in patients with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria". Malaria Journal 7 (1): 225. October 2008. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-7-225. PMID 18973702.
- ↑ "Use of high-density tiling microarrays to identify mutations globally and elucidate mechanisms of drug resistance in Plasmodium falciparum". Genome Biology 10 (2): R21. February 2009. doi:10.1186/gb-2009-10-2-r21. PMID 19216790.
 |
