Chemistry:GKT-831
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
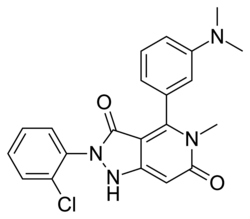
| Formula | C21H19ClN4O2 |
| Molar mass | 394.86 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
GKT-831 (formerly GKT137831) is an orally bioavailable dual inhibitor of NADPH oxidase isoforms NOX4 and NOX1. GKT-831 is a new chemical entity, member of the pyrazolopyridine dione chemical series. The compound is currently the only specific NOX inhibitor that has entered into clinical trials. GKT-831 has demonstrated biological activity in a number of in vitro and in vivo pharmacological models[1][2][3][4][5][6][7] including diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy, atherosclerosis, liver fibrosis, osteoporosis, pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. GKT-831 is currently developed by Genkyotex, a French biotech company based in Toulouse.
Strategy of development
The strategy of development of GKT-831 was initially focused on the treatment of fibrosis and particularly idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a life-threatening disease. GKT-831 obtained orphan drug designation from regulatory agencies in US and EU in early 2010.[8] Despite excellent in vitro and in vivo pharmacology results obtained in preclinical pharmacological models of fibrosis and IPF, and promising phase 1 data showing low toxicity of GKT-831, the company Genkyotex decided to initiate a phase 2 Proof-of-concept in the complex indication of diabetic nephropathy in 2014. As a result, GKT-831 did not reach primary clinical end point and the compound failed to make any significant reduction in albuminuria.[9] Thereafter, the company decided to refocus development to initial clinical applications in fibrosis. In May 2017, Genkyotex announced FDA approval of IND for phase 2 clinical trials in patients with primary biliary cholangitis with extended treatment duration and large study size potentially allowing to assess the effects of GKT-831 on liver inflammation and fibrosis.[10]
History
GKT-831 was discovered in early 2000s by scientists at Genkyotex and invented by a team led by Patrick Page.[11] The compound was patented in 2007 by Genkyotex.[12] GKT-831 was initially developed for Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and obtained orphan drug designation both by FDA and EMEA by end of 2010.[13] GKT-831 was developed by rational drug design following a campaign of high-throughput screening on several NOX isoforms. The initial lead compound GKT136901, a pyrazolopyridine dione derivative was further structurally modified in order to enhance binding affinity and improve pharmacokinetic properties, resulting in the discovery of GKT-831.
References
- ↑ Deliyanti, Devy; Wilkinson-Berka, Jennifer L. (2015-07-30). "Inhibition of NOX1/4 with GKT137831: a potential novel treatment to attenuate neuroglial cell inflammation in the retina". Journal of Neuroinflammation 12: 136. doi:10.1186/s12974-015-0363-z. ISSN 1742-2094. PMID 26219952.
- ↑ Somanna, Naveen K.; Valente, Anthony J.; Krenz, Maike; Fay, William P.; Delafontaine, Patrice; Chandrasekar, Bysani (2016-05-01). "The Nox1/4 Dual Inhibitor GKT137831 or Nox4 Knockdown Inhibits Angiotensin-II-Induced Adult Mouse Cardiac Fibroblast Proliferation and Migration. AT1 Physically Associates With Nox4". Journal of Cellular Physiology 231 (5): 1130–1141. doi:10.1002/jcp.25210. ISSN 1097-4652. PMID 26445208.
- ↑ Asensio-López, Mari C.; Soler, Fernando; Sánchez-Más, Jesús; Pascual-Figal, Domingo; Fernández-Belda, Francisco; Lax, Antonio (2016-03-15). "Early oxidative damage induced by doxorubicin: Source of production, protection by GKT137831 and effect on Ca(2+) transporters in HL-1 cardiomyocytes". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 594: 26–36. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.021. ISSN 1096-0384. PMID 26906075.
- ↑ Gray, Stephen P.; Jha, Jay C.; Kennedy, Kit; van Bommel, Erik; Chew, Phyllis; Szyndralewiez, Cedric; Touyz, Rhian M.; Schmidt, Harald H. H. W. et al. (2017-05-01). "Combined NOX1/4 inhibition with GKT137831 in mice provides dose-dependent reno- and atheroprotection even in established micro- and macrovascular disease". Diabetologia 60 (5): 927–937. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4215-5. ISSN 1432-0428. PMID 28160092.
- ↑ Aoyama, Tomonori; Paik, Yong-Han; Watanabe, Sumio; Laleu, Benoît; Gaggini, Francesca; Fioraso-Cartier, Laetitia; Molango, Sophie; Heitz, Freddy et al. (2012-12-01). "Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in experimental liver fibrosis: GKT137831 as a novel potential therapeutic agent". Hepatology 56 (6): 2316–2327. doi:10.1002/hep.25938. ISSN 1527-3350. PMID 22806357.
- ↑ Jiang, Joy X.; Chen, Xiangling; Serizawa, Nobuko; Szyndralewiez, Cédric; Page, Patrick; Schröder, Katrin; Brandes, Ralf P.; Devaraj, Sridevi et al. (2012-07-15). "Liver fibrosis and hepatocyte apoptosis are attenuated by GKT137831, a novel NOX4/NOX1 inhibitor in vivo". Free Radical Biology & Medicine 53 (2): 289–296. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.05.007. ISSN 1873-4596. PMID 22618020.
- ↑ Green, David E.; Murphy, Tamara C.; Kang, Bum-Yong; Kleinhenz, Jennifer M.; Szyndralewiez, Cédric; Page, Patrick; Sutliff, Roy L.; Hart, C. Michael (2012-11-01). "The Nox4 inhibitor GKT137831 attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular cell proliferation". American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 47 (5): 718–726. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2011-0418OC. ISSN 1535-4989. PMID 22904198.
- ↑ "FDA granting Genkyotex Orphan Drug Designation of GKT137831 for IPF - Genkyotex S.A." (in en). http://pauahosting.co.nz/genkyotex/index.cfm/news-events/fda-granting-genkyotex-orphan-drug-designation-of-gkt137831-for-ipf/.
- ↑ "Genkyotex' NOX inhibitor candidate Fails to follow through on Phase II" (in en-US). Labiotech.eu. 2015-09-10. http://labiotech.eu/genkyotex-fail-nox-inhibitor-candidate-doesnt-follow-through-on-phase-ii-timeline/.
- ↑ "French Biotech gets a Second Opportunity to Fight Liver Fibrosis" (in en-US). Labiotech.eu. 2017-05-03. http://labiotech.eu/genkyotex-nox-enzyme-liver-fibrosis/.
- ↑ "Patrick Page - Chief Development Officer @ Genkyotex | crunchbase". https://www.crunchbase.com/person/patrick-page#/entity.
- ↑ "espacenet patent" (in en-gb). https://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/biblio?II=0&ND=3&adjacent=true&locale=fr_EP&FT=D&date=20170104&CC=CY&NR=1115633T1&KC=T1#.
- ↑ "FDA granting Genkyotex Orphan Drug Designation of GKT137831 for IPF - Genkyotex S.A." (in en). http://pauahosting.co.nz/genkyotex/index.cfm/news-events/fda-granting-genkyotex-orphan-drug-designation-of-gkt137831-for-ipf/.

