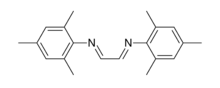
Chemistry:Glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine)
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trimethyl-N-[(2E)-2-[(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imino]ethylidene]aniline
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H24N2 | |
| Molar mass | 292.426 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine) is an organic compound with the formula H2C2(NC6H2Me3)2 (Me = methyl). It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is classified as a diimine ligand. It is used in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. It is synthesized by condensation of 2,4,6-trimethylaniline and glyoxal. In addition to its direct use as a ligand, it is a precursor to imidazole precursors to the popular NHC ligand called IMes.[1][2]
Related compounds
- Glyoxal-bis(triisopropylphenylimine), which is bulkier than glyoxal-bis(mesitylimine).
References
- ↑ Ison, Elon A.; Ison, Ana (2012). "Synthesis of Well-Defined CopperN-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes and Their Use as Catalysts for a "Click Reaction": A Multistep Experiment That Emphasizes the Role of Catalysis in Green Chemistry". Journal of Chemical Education 89 (12): 1575–1577. doi:10.1021/ed300243s. Bibcode: 2012JChEd..89.1575I.
- ↑ Ritleng, Vincent; Brenne, Eric; Chetcuti, Michael J. (2008). "Preparation of a N-Heterocyclic Carbene Nickel(II) Complex. Synthetic Experiments in Current Organic and Organometallic Chemistry". J. Chem. Educ. 85: 1646. doi:10.1021/ed085p1646.
- ↑ Chen, Junting; Ritter, Tobias (2019). "Late-Stage Deoxyfluorination of Phenols with PhenoFluorMix". Org. Synth. 96: 16. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.096.0016.
 |


