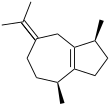
Chemistry:Guaiene
From HandWiki
| |||
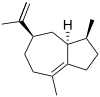 δ-Guaiene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
α: (1S,4S,7R)-1,4-Dimethyl-7-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroazulene
β: (1S,4S)-1,4-Dimethyl-7-(propan-2-ylidene)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroazulene δ: (3S,3aS,5R)-3,8-Dimethyl-5-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-1,2,3,3a,4,5,6,7-octahydroazulene | |||
| Other names
Guajene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C15H24 | |||
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | α: 281-282 °C[1] α: 78-79 °C (@ 2.5 Torr)[2] β: 281 °C[3] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
Guaienes are a series of closely related natural chemical compounds that have been isolated from a variety of plant sources. The guaienes are sesquiterpenes with the molecular formula C15H24. α-Guaiene is the most common and was first isolated from guaiac wood oil from Bulnesia sarmientoi.[4] The guaienes are used in the fragrance and flavoring industries to impart earthy, spicy aromas and tastes.[1][5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Alpha-guaiene, The Good Scents Company
- ↑ Takeda, Kenichi (1961). "Studies on sesquiterpenoids—III, Some derivatives of guaiol". Tetrahedron 13 (4): 308–318. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92224-0.
- ↑ Won, Mi-Mi (2009). Analytica Chimica Acta. 631. pp. 54–61.
- ↑ Bates, R. B.; Slagel, R. C. (1962). "Terpenoids. VI. β-Bulnesene, α-guaiene, β-patchoulene, and guaioxide in essential oils". Chemistry & Industry: 1715–1716.
- ↑ Guaiene, Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives
 |