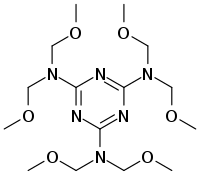
Chemistry:Hexamethoxymethylmelamine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
N2,N2,N4,N4,N6,N6-Hexakis(methoxymethyl)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine | |
| Other names
Hexamethylolemelamine
Hexakis(methoxymethyl)melamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H30N6O6 | |
| Molar mass | 390.441 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 40–42 °C (104–108 °F; 313–315 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H317, H319, H341, H351 | |
| P264, P280, P305+351+338, P337+313 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexa(methoxymethyl)melamine (HMMM) is a hemiaminal ether commonly used as a crosslinking agent in the production of coatings and rubber items. It is produced via the reaction of melamine with formaldehyde and excess methanol, with the later also acting as a solvent for the reaction. It can be considered as a monomeric intermediate in the formation of melamine resin.
Hexamethoxymethylmelamine is used along with resorcinol in the production of vehicle tires, where it improves adhesion between the rubber and the steel reinforcing cords. As it has some water solubility it slowly leaches out of the rubber; particularly from the particles formed as the tires wear-down through use.[3][4] Road runoff then introduces it into urban waters, where it has become a contaminant of emerging concern.[5][6][7]
See also
- Rubber pollution
References
- ↑ "Hexa(methoxymethyl)melamine" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/62479#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ "C&L Inventory". European Chemicals Agency. https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/50601.
- ↑ Johannessen, Cassandra; Parnis, J. Mark (October 2021). "Environmental modelling of hexamethoxymethylmelamine, its transformation products, and precursor compounds: An emerging family of contaminants from tire wear". Chemosphere 280: 130914. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130914.
- ↑ Johannessen, Cassandra; Helm, Paul; Metcalfe, Chris D. (January 2021). "Runoff of the Tire-Wear Compound, Hexamethoxymethyl-Melamine into Urban Watersheds". Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 82: 162–170. doi:10.1007/s00244-021-00815-5.
- ↑ Tian, Zhenyu; Peter, Katherine T.; Gipe, Alex D.; Zhao, Haoqi; Hou, Fan; Wark, David A.; Khangaonkar, Tarang; Kolodziej, Edward P. et al. (21 January 2020). "Suspect and Nontarget Screening for Contaminants of Emerging Concern in an Urban Estuary". Environmental Science & Technology 54 (2): 889–901. doi:10.1021/acs.est.9b06126. PMID 31887037. Bibcode: 2020EnST...54..889T.
- ↑ Johannessen, Cassandra; Helm, Paul; Metcalfe, Chris D. (October 2021). "Detection of selected tire wear compounds in urban receiving waters". Environmental Pollution 287: 117659. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117659. PMID 34426371.
- ↑ Seiwert, Bettina; Klöckner, Philipp; Wagner, Stephan; Reemtsma, Thorsten (August 2020). "Source-related smart suspect screening in the aqueous environment: search for tire-derived persistent and mobile trace organic contaminants in surface waters". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 412 (20): 4909–4919. doi:10.1007/s00216-020-02653-1. PMID 32382968.
 |

