Chemistry:Isobornyl acetate
From HandWiki
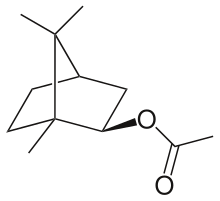
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(1S,2S,4S)-1,7,7-trimethyl-2-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl] acetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 196.290 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.9841 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 102–103 °C (216–217 °F; 375–376 K) 13 torr |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isobornyl acetate is an organic compound consisting of the acetate ester or the terpenoid isoborneol. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant pine-like scent, and it is produced on a multi-ton scale for this purpose. The compound is prepared by reaction of camphene with acetic acid in the presence of a strongly acidic catalyst such as sulfuric acid. Hydrolysis of isobornyl acetate gives isoborneol, a precursor to camphor.[1]
Like many plant exudates, isobornyl acetate appears to have antifeedant properties.[2]
References
 |
- ↑ Panten, Johannes; Surburg, Horst (2015). "Flavors and Fragrances, 2. Aliphatic Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. pp. 1–55. doi:10.1002/14356007.t11_t01. ISBN 9783527306732.
- ↑ Andrews, R. E.; Parks, L. W.; Spence, K. D. (1980). "Some Effects of Douglas Fir Terpenes on Certain Microorganisms". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 40 (2): 301–304. doi:10.1128/aem.40.2.301-304.1980. PMID 16345609. Bibcode: 1980ApEnM..40..301A.

