Chemistry:LY-341495
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
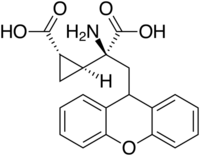
| Other names | (2S)-2-Amino-2-[(1S,2S)-2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl]-3-(xanth-9-yl)propanoic acid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H19NO5 |
| Molar mass | 353.374 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
LY-341495 is a research drug developed by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly, which acts as a potent and selective orthosteric antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3).[1][2][3][4]
It is used in scientific research in several different areas, showing antidepressant effects in animal models,[5][6][7][8] increasing the behavioural effects of hallucinogenic drugs in animal tests,[9][10][11][12] and increasing the analgesic effects of μ-opioid agonists,[13][14] as well as modulating dopamine receptor function.[15][16][17]
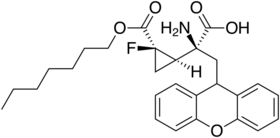
The 1-fluorocyclopropane analog has a superior pharmacokinetic profile and similar mGluR2/3 affinity, and making a prodrug from this with the heptyl ester increases bioavailability still further.[18]
See also
References
- ↑ "2-substituted (2SR)-2-amino-2-((1SR,2SR)-2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl)glycines as potent and selective antagonists of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. 2. Effects of aromatic substitution, pharmacological characterization, and bioavailability". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 41 (3): 358–78. January 1998. doi:10.1021/jm970498o. PMID 9464367.
- ↑ "LY341495 is a nanomolar potent and selective antagonist of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors". Neuropharmacology 37 (1): 1–12. 1998. doi:10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00191-3. PMID 9680254.
- ↑ "The potent mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 identifies roles for both cloned and novel mGlu receptors in hippocampal synaptic plasticity". Neuropharmacology 37 (12): 1445–58. December 1998. doi:10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00145-2. PMID 9886667.
- ↑ "[3H]-LY341495 as a novel antagonist radioligand for group II metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptors: characterization of binding to membranes of mGlu receptor subtype expressing cells". Neuropharmacology 38 (10): 1519–29. October 1999. doi:10.1016/s0028-3908(99)00053-2. PMID 10530814.
- ↑ "Mood disorders: regulation by metabotropic glutamate receptors". Biochemical Pharmacology 75 (5): 997–1006. March 2008. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.09.021. PMID 18164691.
- ↑ "Group-II metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands as adjunctive drugs in the treatment of depression: a new strategy to shorten the latency of antidepressant medication?". Molecular Psychiatry 12 (8): 704–6. August 2007. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4002005. PMID 17653204.
- ↑ "Requirement of AMPA receptor stimulation for the sustained antidepressant activity of ketamine and LY341495 during the forced swim test in rats". Behavioural Brain Research 271: 111–5. September 2014. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2014.05.065. PMID 24909673.
- ↑ "Fast-acting antidepressants rapidly stimulate ERK signaling and BDNF release in primary neuronal cultures". Neuropharmacology 111: 242–252. December 2016. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.09.011. PMID 27634096.
- ↑ "Behavioral evidence for interactions between a hallucinogenic drug and group II metabotropic glutamate receptors". Neuropsychopharmacology 23 (5): 569–76. November 2000. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00136-6. PMID 11027922.
- ↑ "A selective positive allosteric modulator of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 2 blocks a hallucinogenic drug model of psychosis". Molecular Pharmacology 72 (2): 477–84. August 2007. doi:10.1124/mol.107.035170. PMID 17526600.
- ↑ "The role of 5-HT2A, 5-HT 2C and mGlu2 receptors in the behavioral effects of tryptamine hallucinogens N,N-dimethyltryptamine and N,N-diisopropyltryptamine in rats and mice". Psychopharmacology 232 (1): 275–84. January 2015. doi:10.1007/s00213-014-3658-3. PMID 24985890.
- ↑ "Crosstalk Between 5-HT2A and mGlu2 Receptors: Implications in Schizophrenia and Its Treatment". 5-HT2A Receptors in the Central Nervous System. The Receptors. 32. 2018. pp. 147–189. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-70474-6_7. ISBN 978-3-319-70472-2.
- ↑ "Increased efficacy of micro-opioid agonist-induced antinociception by metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists in C57BL/6 mice: comparison with (-)-6-phosphonomethyl-deca-hydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (LY235959)". Psychopharmacology 198 (2): 271–8. June 2008. doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1130-y. PMID 18392754.
- ↑ "Morphine in combination with metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on schedule-controlled responding and thermal nociception". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 324 (2): 732–9. February 2008. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.131417. PMID 17982001.
- ↑ "Group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists LY341495 and LY366457 increase locomotor activity in mice". Neuropharmacology 45 (5): 565–74. October 2003. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(03)00232-6. PMID 12941370.
- ↑ "Blockade of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens produces hyperlocomotion in rats previously exposed to amphetamine". Neuropharmacology 51 (5): 986–92. October 2006. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.06.008. PMID 16901517.
- ↑ "Blockade of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors produces hyper-locomotion in cocaine pre-exposed rats by interactions with dopamine receptors". Neuropharmacology 55 (4): 555–9. September 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.012. PMID 18675831.
- ↑ "Synthesis, in vitro pharmacology, and pharmacokinetic profiles of 2-[1-amino-1-carboxy-2-(9H-xanthen-9-yl)-ethyl]-1-fluorocyclopropanecarboxylic acid and its 6-heptyl ester, a potent mGluR2 antagonist". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16 (8): 4359–66. April 2008. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.02.066. PMID 18348906.
 |