Chemistry:Levomoramide
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
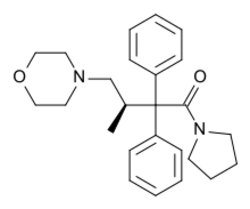 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H32N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 392.534 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Levomoramide is the inactive isomer of the opioid analgesic dextromoramide, invented by the chemist Paul Janssen in 1956. Unlike dextromoramide, which is a potent analgesic with high abuse potential, levomoramide is virtually without activity.[1][2]
"Resolution reveals that the analgetic activity in this case resides almost entirely in the (+) isomer."[3]
"In the α-CH3 series, one of the optical isomers of each enantiomorphic pair is about twice as active as the racemic mixture; the other isomer is devoid of significant analgesic activity."[4]
However, despite being inactive, levomoramide is scheduled by United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs.
References
- ↑ "A new series of potent analgesics.". Journal of the American Chemical Society 78 (15): 3862. August 1956. doi:10.1021/ja01596a087.
- ↑ "A new series of potent analgesics.". Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 9 (1): 381–400. September 1957. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1957.tb12290.x.
- ↑ Lednicer, Daniel (1982). Central Analgetics. Wiley. p. 194. ISBN 0-471-08314-3.
- ↑ Synthetic Analgesics Part 1: Diphenylpropylamines. Pergamon Press. 1960. p. 143.
pl:Moramid
 |

