Chemistry:Lisofylline
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
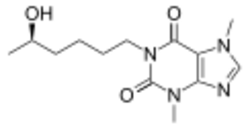
| Other names | 1-(5-Hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine (HDX) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H20N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 280.328 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lisofylline (LSF) is a synthetic small molecule with novel anti-inflammatory properties. LSF can effectively prevent type 1 diabetes in preclinical models and improves the function and viability of isolated or transplanted pancreatic islets. It is a metabolite of pentoxifylline.
As well, LSF improves cellular mitochondrial function and blocks interleukin-12 (IL-12) signaling and STAT-4 activation in target cells and tissues. IL-12 and STAT-4 activation are important pathways linked to inflammation and autoimmune damage to insulin producing cells. Therefore, LSF and related analogs could provide a new therapeutic approach to prevent or reverse type 1 diabetes. LSF also directly reduces glucose-induced changes in human kidney cells suggesting that LSF and analogs have the potential to treat the complications associated with diabetes.
Synthesis
The R enantiomer of the pentoxyfylline analogue in which the ketone has been reduced to an alcohol shows enhanced activity as an inhibitor of acetyl CoA over the parent drug.

For analogs see:[8]
Further reading
- Aretz, Werner; Harald Furrer & Ulrich Gebert et al., "Verfahren zur enantioselektiven Darstellung von (ω-1)-Hydroxyalkylxanthinen [Method for the enantioselective preparation of(ω-1)-hydroxyalkylxanthines]", DE patent 3942872, published 1991-06-27
- Aretz, Werner; Harald Furrer & Ulrich Gebert et al., "Process for the enantioselective preparation of (β-1)-hydroxyalkylxanthines by reduction using Rhodotorula rubra", US patent 5310666, published 1994-05-10
- Klein, J. Peter; Alistair J. Leigh & John Michnick et al., "Asymmetric synthesis of chiral secondary alcohols", WO patent 9531450, published 1995-11-23
References
- ↑ "99% Chirally selective synthesis via pinanediol boronic esters: Insect pheromones, diols, and an amino alcohol". Journal of the American Chemical Society 108 (4): 810. 1986. doi:10.1021/ja00264a039.
- ↑ "Directed chiral synthesis with pinanediol boronic esters". Journal of the American Chemical Society 102 (25): 7590. 1980. doi:10.1021/ja00545a046.
- ↑ "Asymmetric synthesis of alkylarylcarbinols via reaction of a chiral pinanediol alkylboronic ester with arylmethyl chlorides". Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 8 (23): 3843. 1997. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(97)00565-X.
- ↑ "Synthesis and properties of pinanediol .alpha.-amido boronic esters". Organometallics 3 (8): 1284. 1984. doi:10.1021/om00086a024.
- ↑ "Asymmetric synthesis with boronic esters". Accounts of Chemical Research 21 (8): 294–300. 1988. doi:10.1021/ar00152a002.
- ↑ "Boronic esters in asymmetric synthesis". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 78 (20): 10009–23. October 2013. doi:10.1021/jo4013942. PMID 23875690.
- ↑ "Highly enantioselective synthesis of tertiary boronic esters and their stereospecific conversion to other functional groups and quaternary stereocentres". Chemistry: A European Journal 17 (47): 13124–32. November 2011. doi:10.1002/chem.201102581. PMID 22052475.
- ↑ "Synthesis and biological evaluation of lisofylline (LSF) analogs as a potential treatment for Type 1 diabetes". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 16 (13): 3401–5. July 2006. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.04.036. PMID 16650991.
External links
- University of Virginia Research Announcement
- National Institute of Health on Lisofylline
- Metabolism of lisofylline in the human liver
 |
