Chemistry:Mertansine
Mertansine, also called DM1 (and in some of its forms emtansine), is a thiol-containing maytansinoid that for therapeutic purposes is attached to a monoclonal antibody through reaction of the thiol group with a linker structure to create an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC).[1]
ADCs with this design include trastuzumab emtansine, lorvotuzumab mertansine, and cantuzumab mertansine. Some are still experimental; others are in regular clinical use.[citation needed]
Mechanism of action
Mertansine is a tubulin inhibitor, meaning that it inhibits the assembly of microtubules by binding to tubulin (at the rhizoxin binding site).[2]
The monoclonal antibody binds specifically to a structure (usually a protein) occurring in a tumour, thus directing mertansine into this tumour. This concept is called targeted therapy.[citation needed]
Uses and chemistry
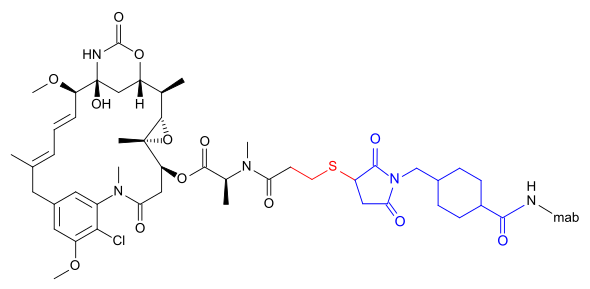
The following (experimental) drugs are antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) combining monoclonal antibodies with mertansine as the cytotoxic component. Mertansine is linked via 4-mercaptovaleric acid.[3]
ADCs include:
- Bivatuzumab mertansine
- Cantuzumab mertansine[4]
- Lorvotuzumab mertansine (IMGN901) for CD56 positive cancers, for example multiple myeloma[5]

Emtansine
DM1 can also be linked via a more complicated structure – 4-(3-mercapto-2,5-dioxo-1-pyrrolidinylmethyl)-cylohexanecarboxylic acid or SMCC –, in which case the International Nonproprietary Name of the conjugate formed contains the word emtansine. The abbreviation comes from the chemical designation "succinimidyl-trans-4-(maleimidylmethyl) cyclohexane-1-carboxylate" which is used in the primary literature[6] as well as by the World Health Organization (WHO)[7] despite the fact that the linker contains only one imide group according to the WHO.[3]
DM1 and its attachment via these linkers result from ImmunoGen Inc research.
An example is:
- Trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1), an anti-HER2/neu antibody-drug conjugate[8][9]
References
- ↑ Zámečník, Josef (2019). "18 – Prediktivní patologie" (in cs). Patologie. 1. Praha: PRAGER PUBLISHING. p. 276. ISBN 978-80-270-6457-1.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute: Definition of Maytansine
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances: Names for radicals, groups & others. WHO. 2012. pp. 66f. https://www.who.int/medicines/services/inn/Radical_Book_2012.pdf.
- ↑ International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN): List 89. WHO. 2003. p. 188. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/PL89.pdf.
- ↑ "ImmunoGen reports encouraging clinical data of IMGN901". The Medical News. 6 December 2009. https://www.news-medical.net/news/20091206/ImmunoGen-reports-encouraging-clinical-data-of-IMGN901.aspx.
- ↑ Girish, Sandhya; Gupta, Manish; Wang, Bei; Lu, Dan; Krop, Ian E.; Vogel, Charles L.; Burris Iii, Howard A.; Lorusso, Patricia M. et al. (May 2012). "Clinical pharmacology of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1): an antibody–drug conjugate in development for the treatment of HER2-positive cancer". Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69 (5): 1229–1240. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1817-3. PMID 22271209.
- ↑ International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN): List 103. WHO. 2010. p. 172. https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/INN_PL103.pdf.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute: trastuzumab-MCC-DM1 antibody-drug conjugate
- ↑ ImmunoGen: Trastuzumab-DM1
 |
