Chemistry:Myxothiazol
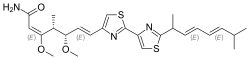
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
7-{2'-[(1S,2E,4E)-1,6-Dimethyl-2,4-heptadienyl]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Myxothiazol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H33N3O3S2 | |
| Molar mass | 487.68 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Myxothiazol is a chemical compound produced by the myxobacterium Myxococcus fulvus. It is an inhibitor of the mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex (coenzyme Q - cytochrome c reductase).[1][2]
Myxothiazol is a competitive inhibitor of ubiquinol, and binds at the quinol oxidation (Qo) site of the bc1 complex, blocking electron transfer to the Rieske iron-sulfur protein. Binding of myxothiazol induces a red-shift to the visible absorption spectrum of reduced haem bl. In contrast to stigmatellin, myxothiazol does not form a hydrogen bond to the Rieske iron-sulfur protein, binding instead in the 'b-proximal' region of the cytochrome bQo site. Movement of the cytoplasmic domain of the Rieske protein is therefore unaffected by the binding of this inhibitor.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Georg Thierbach, Hans Reichenbach (1981). "Myxothiazol, a new antibiotic interfering with respiration". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 19 (4): 504–507. doi:10.1128/AAC.19.4.504. PMID 7247372.
- ↑ Gebhard von Jagow, W. D. Engel (1981). "Complete Inhibition of Electron Transfer from Ubiquinol to Cytochrome by the Combined Action of Antimycin and Myxothiazol". FEBS Letters 136 (1): 19–24. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(81)81206-9. PMID 7319059.
 |

