Chemistry:N-Acetyldopamine
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 195.218 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
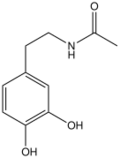
N-Acetyldopamine is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)NHCH2CH2C6H3(OH)2. It is the N-acetylated derivative of dopamine. This compound is a reactive intermediate in sclerotization, the process by which insect cuticles are formed by hardening molecular precursors. The catechol substituent is susceptible to redox and crosslinking.[2][3]
References
- ↑ "N-Acetyldopamine" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/100526#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Andersen, Svend Olav (2010). "Insect cuticular sclerotization: A review". Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 40 (3): 166–178. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.10.007. PMID 19932179.
- ↑ Kramer, Karl J.; Kanost, Michael R.; Hopkins, Theodore L.; Jiang, Haobo; Zhu, Yu Cheng; Xu, Rongda; Kerwin, J.L; Turecek, F. (2001). "Oxidative conjugation of catechols with proteins in insect skeletal systems". Tetrahedron 57 (2): 385–392. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(00)00949-2.
 |

